Page 44 - Understanding Flight
P. 44
CH02_Anderson 7/25/01 8:55 AM Page 31
How Airplanes Fly 31
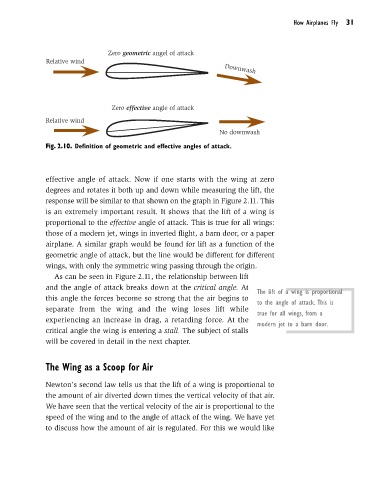
Zero geometric angel of attack
Relative wind Downwash
Zero effective angle of attack
Relative wind
No downwash
Fig. 2.10. Definition of geometric and effective angles of attack.
effective angle of attack. Now if one starts with the wing at zero
degrees and rotates it both up and down while measuring the lift, the
response will be similar to that shown on the graph in Figure 2.11. This
is an extremely important result. It shows that the lift of a wing is
proportional to the effective angle of attack. This is true for all wings:
those of a modern jet, wings in inverted flight, a barn door, or a paper
airplane. A similar graph would be found for lift as a function of the
geometric angle of attack, but the line would be different for different
wings, with only the symmetric wing passing through the origin.
As can be seen in Figure 2.11, the relationship between lift
and the angle of attack breaks down at the critical angle. At
The lift of a wing is proportional
this angle the forces become so strong that the air begins to
to the angle of attack. This is
separate from the wing and the wing loses lift while
true for all wings, from a
experiencing an increase in drag, a retarding force. At the
modern jet to a barn door.
critical angle the wing is entering a stall. The subject of stalls
will be covered in detail in the next chapter.
The Wing as a Scoop for Air
Newton’s second law tells us that the lift of a wing is proportional to
the amount of air diverted down times the vertical velocity of that air.
We have seen that the vertical velocity of the air is proportional to the
speed of the wing and to the angle of attack of the wing. We have yet
to discuss how the amount of air is regulated. For this we would like