Page 76 - Understanding Flight
P. 76
CH03_Anderson 7/25/01 8:56 AM Page 63
Wings 63
2
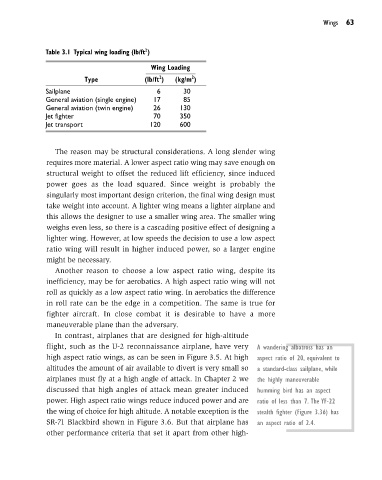
Table 3.1 Typical wing loading (lb/ft )
Wing Loading
2
2
Type (lb/ft ) (kg/m )
Sailplane 6 30
General aviation (single engine) 17 85
General aviation (twin engine) 26 130
Jet fighter 70 350
Jet transport 120 600
The reason may be structural considerations. A long slender wing
requires more material. A lower aspect ratio wing may save enough on
structural weight to offset the reduced lift efficiency, since induced
power goes as the load squared. Since weight is probably the
singularly most important design criterion, the final wing design must
take weight into account. A lighter wing means a lighter airplane and
this allows the designer to use a smaller wing area. The smaller wing
weighs even less, so there is a cascading positive effect of designing a
lighter wing. However, at low speeds the decision to use a low aspect
ratio wing will result in higher induced power, so a larger engine
might be necessary.
Another reason to choose a low aspect ratio wing, despite its
inefficiency, may be for aerobatics. A high aspect ratio wing will not
roll as quickly as a low aspect ratio wing. In aerobatics the difference
in roll rate can be the edge in a competition. The same is true for
fighter aircraft. In close combat it is desirable to have a more
maneuverable plane than the adversary.
In contrast, airplanes that are designed for high-altitude
flight, such as the U-2 reconnaissance airplane, have very A wandering albatross has an
high aspect ratio wings, as can be seen in Figure 3.5. At high aspect ratio of 20, equivalent to
altitudes the amount of air available to divert is very small so a standard-class sailplane, while
airplanes must fly at a high angle of attack. In Chapter 2 we the highly maneuverable
discussed that high angles of attack mean greater induced humming bird has an aspect
power. High aspect ratio wings reduce induced power and are ratio of less than 7. The YF-22
the wing of choice for high altitude. A notable exception is the stealth fighter (Figure 3.36) has
SR-71 Blackbird shown in Figure 3.6. But that airplane has an aspect ratio of 2.4.
other performance criteria that set it apart from other high-