Page 232 - Valve Selection Handbook
P. 232
Rupture Discs 219
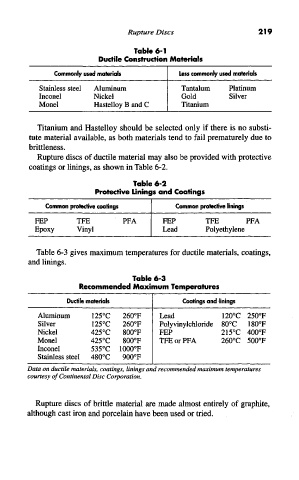
Table 6-1
Ductile Construction Materials
Commonly used materials Less commonly used materials
Stainless steel Aluminum Tantalum Platinum
Inconel Nickel Gold Silver
Monel Hastelloy B and C Titanium
Titanium and Hastelloy should be selected only if there is no substi-
tute material available, as both materials tend to fail prematurely due to
brittleness.
Rupture discs of ductile material may also be provided with protective
coatings or linings, as shown in Table 6-2.
Table 6-2
Protective Linings and Coatings
Common protective coatings Common protective linings
FEP TFE PFA FEP TFE PFA
Epoxy Vinyl Lead Polyethylene
Table 6-3 gives maximum temperatures for ductile materials, coatings,
and linings.
Table 6-3
Recommended Maximum Temperatures
Ductile materials Coatings and linings
Aluminum 125°C 260°F Lead 120°C 250°F
Silver 125°C 260°F Polyvinylchloride 80°C 180°F
Nickel 425°C 800°F FEP 215°C 400°F
Monel 425°C 800°F TFE or PFA 260°C 500°F
Inconel 535°C 1000°F
Stainless steel 480°C 900°F
Data on ductile materials, coatings, linings and recommended maximum temperatures
courtesy of Continental Disc Corporation.
Rupture discs of brittle material are made almost entirely of graphite,
although cast iron and porcelain have been used or tried.