Page 310 - Valve Selection Handbook
P. 310
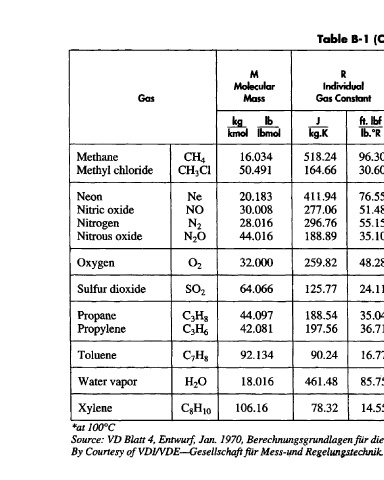
Table B-l (Continued)
PC
M R Isentropic T c Critical
Molecular Individual Coefficient Critical Pressure
Gas Mass Gas Constant kfor Temperature (absolute)
P -»atm
kg Ib J ft.lbf T = 273K
Icmol Ibmol kg.K lb.°R =492R °K °R MPa Ib/in 2
Methane CH 4 16.034 518.24 96.30 1.31 190.7 343.3 4.629 671.2
Methyl chloride CH 3C1 50.491 164.66 30.60 — 416.2 749.2 6.669 667.0
Neon Ne 20.183 411.94 76.55 1.64 44.4 79.9 2.654 384.8
Nitric oxide NO 30.008 277.06 51.48 1.39 180.2 324.4 6.541 948.5
Nitrogen N 2 28.016 296.76 55.15 1.40 126.3 227.3 3.383 490.6
Nitrous oxide N 2 O 44.016 188.89 35.10 1.28 309.7 557.5 7.267 1053.7
Oxygen O 2 32.000 259.82 48.28 1.40 154.77 278.6 5.080 736.6
Sulfur dioxide SO 2 64.066 125.77 24.11 1.28 430.7 775.3 7.885 1143.3
Propane C 3H 8 44.097 188.54 35.04 — 370.0 666.0 4.256 617.15
Propylene C 3H6 42.081 197.56 36.71 — 364.91 656.8 4.621 670.1
Toluene C 7H 8 92.134 90.24 16.77 — 593.8 1068.8 4.207 610.0
Water vapor H 2O 18.016 461.48 85.75 1.33* 647.3 1165.1 22.129 3208.8
Xylene C 8H 10 106.16 78.32 14.55 _ _ _ _ _
*at 100°C
Source: VD Blatt4, Entwurf, Jan. 1970, Berechnungsgrundlagen für die Durchflussmessung mit Drosselgeräten, Stoffwerte.
By Courtesy ofVDI/VDE—-Gesellschaft fürMess-undRegelungstechnik,