Page 56 - Valve Selection Handbook
P. 56
Fundamentals 43
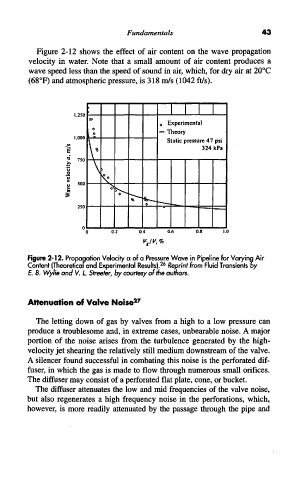
Figure 2-12 shows the effect of air content on the wave propagation
velocity in water. Note that a small amount of air content produces a
wave speed less than the speed of sound in air, which, for dry air at 20°C
(68°F) and atmospheric pressure, is 318 m/s (1042 ft/s).
Figure 2-12. Propagation Velocity a of a Pressure Wave in Pipeline for Varying Air
Content (Theoretical and Experimental Results). 26 Reprint from Fluid Transients by
E. B. Wylie and V. L Streeter, by courtesy of the authors.
Attenuation of Valve Noise 27
The letting down of gas by valves from a high to a low pressure can
produce a troublesome and, in extreme cases, unbearable noise. A major
portion of the noise arises from the turbulence generated by the high-
velocity jet shearing the relatively still medium downstream of the valve.
A silencer found successful in combating this noise is the perforated dif-
fuser, in which the gas is made to flow through numerous small orifices.
The diffuser may consist of a perforated flat plate, cone, or bucket.
The diffuser attenuates the low and mid frequencies of the valve noise,
but also regenerates a high frequency noise in the perforations, which,
however, is more readily attenuated by the passage through the pipe and