Page 101 - Video Coding for Mobile Communications Efficiency, Complexity, and Resilience
P. 101
78 Chapter 3. Video Coding: Standards
2. The BAB is Jagged opaque. In this case, no shape coding is necessary,
but texture information is coded.
3. The BAB is coded without motion compensation using IntraCAE.
4. The MVDs is zero (i.e., MVs = MVPs) and no block update is neces-
sary.
5. The MVDs is zero and the block needs to be updated. In this case,
InterCAE is used for coding the block update.
6. The MVDs is nonzero and no update is necessary.
7. The MVDs is nonzero and the block needs to be updated. In this case,
InterCAE is used for coding the block update.
Modes 1 and 2 require no shape coding. For mode 3, shape is encoded using
IntraCAE. For modes 4 –7, motion estimation and compensation are employed.
The motion vector di1erence for shape (MVDs) is the di1erence between
the shape motion vector (MVs) and its predictor (MVPs). This predictor is
estimated from either neighboring shape motion vectors or co-located texture
motion vectors. When the mode indicates that no update is required, then the
MVs is simply used to copy a displaced 16 × 16 block from the reference
binary alpha plane to the current BAB. If, however, the mode indicates that
an update is required, then the update is coded using InterCAE.
The CAE is a binary arithmetic coding algorithm where the probability of
a symbol is determined from the context of the neighboring symbols. First,
the arithmetic encoder is initialized. The binary pels (elements) of the BAB
are then encoded in raster-scan order using the following steps:
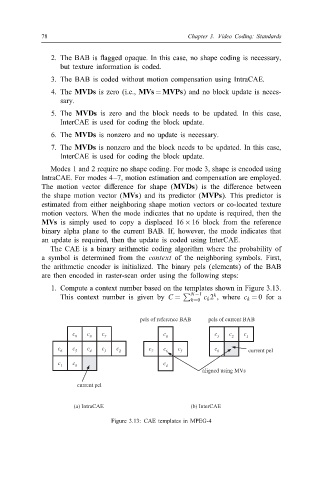
1. Compute a context number based on the templates shown in Figure 3.13.
k
This context number is given by C = � N −1 c k 2 , where c k = 0 for a
k=0
pels of reference BAB pels of current BAB
c 9 c 8 c 7 c 8 c 3 c 2 c 1
c c c c c c c c c
6 5 4 3 2 7 6 5 0 current pel
c c c
1 0 4
aligned using MVs
current pel
(a) IntraCAE (b) InterCAE
Figure 3.13: CAE templates in MPEG-4