Page 187 - Video Coding for Mobile Communications Efficiency, Complexity, and Resilience
P. 187
164 Chapter 7. Reduced-Complexity Motion Estimation Techniques
a b a b a b a b
C B C B
c d c d c d c d
a b a b a b a b D A D A
c d c d c d c d
C B C B
a b a b a b a b
c d c d c d c d D A D A
a b a b a b a b
c d c d c d c d
(a) Four 4:1 subsampling patterns (b) Alternating schedule of four sub-
sampling patterns over the search window
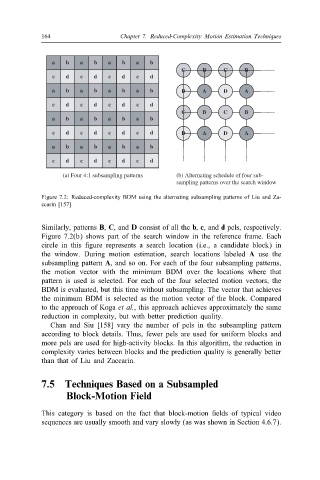
Figure 7.2: Reduced-complexity BDM using the alternating subsampling patterns of Liu and Za-
ccarin [157]
Similarly, patterns B, C, and D consist of all the b, c, and d pels, respectively.
Figure 7.2(b) shows part of the search window in the reference frame. Each
circle in this )gure represents a search location (i.e., a candidate block) in
the window. During motion estimation, search locations labeled A use the
subsampling pattern A, and so on. For each of the four subsampling patterns,
the motion vector with the minimum BDM over the locations where that
pattern is used is selected. For each of the four selected motion vectors, the
BDM is evaluated, but this time without subsampling. The vector that achieves
the minimum BDM is selected as the motion vector of the block. Compared
to the approach of Koga et al., this approach achieves approximately the same
reduction in complexity, but with better prediction quality.
Chan and Siu [158] vary the number of pels in the subsampling pattern
according to block details. Thus, fewer pels are used for uniform blocks and
more pels are used for high-activity blocks. In this algorithm, the reduction in
complexity varies between blocks and the prediction quality is generally better
than that of Liu and Zaccarin.
7.5 Techniques Based on a Subsampled
Block-Motion Field
This category is based on the fact that block-motion )elds of typical video
sequences are usually smooth and vary slowly (as was shown in Section 4.6.7).