Page 267 - Video Coding for Mobile Communications Efficiency, Complexity, and Resilience
P. 267
244 Chapter 10. Error Concealment Using Motion Field Interpolation
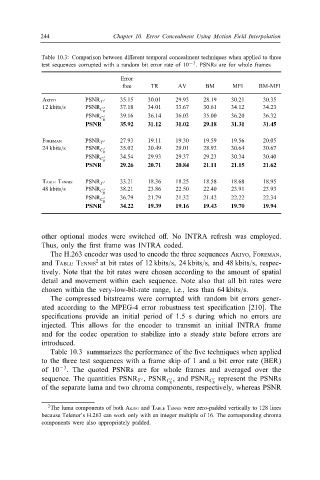
Table 10.3: Comparison between di,erent temporal concealment techniques when applied to three
test sequences corrupted with a random bit error rate of 10 −3 . PSNRs are for whole frames
Error
free TR AV BM MFI BM-MFI
AKIYO PSNR Y � 35.15 30.01 29.93 28.19 30.21 30.35
12 kbits=s PSNR � 37.18 34.01 33.67 30.61 34.12 34.23
C
R
PSNR � 39.16 36.14 36.03 35.00 36.20 36.32
C
B
PSNR 35.92 31.12 31.02 29.18 31.31 31.45
FOREMAN PSNR Y � 27.93 19.11 19.30 19.59 19.56 20.05
24 kbits=s PSNR � 35.02 30.49 29.01 28.92 30.64 30.67
C
R
PSNR � 34.54 29.93 29.37 29.23 30.34 30.40
C
B
PSNR 29.26 20.71 20.84 21.11 21.15 21.62
TABLE TENNIS PSNR Y � 33.21 18.36 18.25 18.58 18.68 18.95
48 kbits=s PSNR � 38.21 23.86 22.50 22.40 23.91 23.93
C
R
PSNR � 36.79 21.79 21.32 21.42 22.22 22.34
C
B
PSNR 34.22 19.39 19.16 19.43 19.70 19.94
other optional modes were switched o,. No INTRA refresh was employed.
Thus, only the $rst frame was INTRA coded.
The H.263 encoder was used to encode the three sequences AKIYO,FOREMAN,
2
and TABLE TENNIS at bit rates of 12 kbits=s, 24 kbits=s, and 48 kbits=s, respec-
tively. Note that the bit rates were chosen according to the amount of spatial
detail and movement within each sequence. Note also that all bit rates were
chosen within the very-low-bit-rate range, i.e., less than 64 kbits=s.
The compressed bitstreams were corrupted with random bit errors gener-
ated according to the MPEG-4 error robustness test speci$cation [210]. The
speci$cations provide an initial period of 1.5 s during which no errors are
injected. This allows for the encoder to transmit an initial INTRA frame
and for the codec operation to stabilize into a steady state before errors are
introduced.
Table 10.3 summarizes the performance of the $ve techniques when applied
to the three test sequences with a frame skip of 1 and a bit error rate (BER)
of 10 −3 . The quoted PSNRs are for whole frames and averaged over the
� , and PSNR C represent the PSNRs
sequence. The quantities PSNR Y � , PSNR C R B �
of the separate luma and two chroma components, respectively, whereas PSNR
2 The luma components of both AKIYO and TABLE TENNIS were zero-padded vertically to 128 lines
because Telenor’s H.263 can workonly with an integer multiple of 16. The corresponding chroma
components were also appropriately padded.