Page 27 - Video Coding for Mobile Communications Efficiency, Complexity, and Resilience
P. 27
4 Chapter 1. Introduction to Mobile Video Communications
It should be emphasized that those are not the only requirements of a mo-
bile video communication system. Requirements like low delay, interactivity,
scalability, and security are equally important.
1.3Possible Solutions
Mobile video communication is a truly interdisciplinary subject [7]. Complete
systems are likely to draw together solutions from diBerent areas, like video
source coding, channel coding, network design, semiconductor design, and oth-
ers. This book will concentrate on solutions based on the video source coding
part of the area. Thus, before being able to present the adopted approach, a
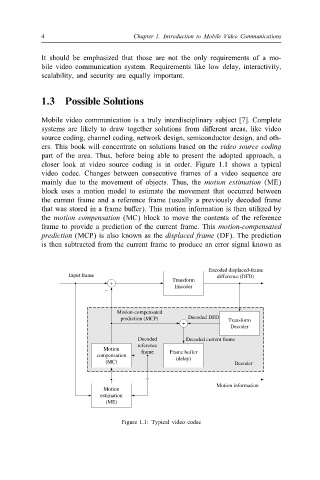
closer look at video source coding is in order. Figure 1.1 shows a typical
video codec. Changes between consecutive frames of a video sequence are
mainly due to the movement of objects. Thus, the motion estimation (ME)
block uses a motion model to estimate the movement that occurred between
the current frame and a reference frame (usually a previously decoded frame
that was stored in a frame buBer). This motion information is then utilized by
the motion compensation (MC) block to move the contents of the reference
frame to provide a prediction of the current frame. This motion-compensated
prediction (MCP) is also known as the displaced frame (DF). The prediction
is then subtracted from the current frame to produce an error signal known as
Encoded displaced-frame
Input frame difference (DFD)
Transform
+
_ Encoder
Motion-compensated
prediction (MCP) Decoded DFD Transform
+
Decoder
Decoded Decoded current frame
reference
Motion frame
compensation Frame buffer
(delay)
(MC) Decoder
Motion information
Motion
estimation
(ME)
Figure 1.1: Typical video codec