Page 64 - Video Coding for Mobile Communications Efficiency, Complexity, and Resilience
P. 64
Section 2.7. Interframe Coding 41
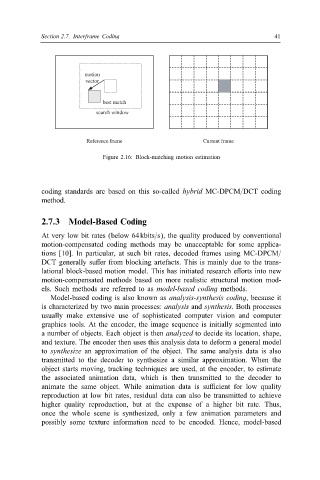
motion
vector
best match
search window
Reference frame Current frame
Figure 2.16: Block-matching motion estimation
coding standards are based on this so-called hybrid MC-DPCM=DCT coding
method.
2.7.3 Model-Based Coding
At very low bit rates (below 64 kbits=s), the quality produced by conventional
motion-compensated coding methods may be unacceptable for some applica-
tions [10]. In particular, at such bit rates, decoded frames using MC-DPCM=
DCT generally su6er from blocking artefacts. This is mainly due to the trans-
lational block-based motion model. This has initiated research e6orts into new
motion-compensated methods based on more realistic structural motion mod-
els. Such methods are referred to as model-based coding methods.
Model-based coding is also known as analysis-synthesis coding, because it
is characterized by two main processes: analysis and synthesis. Both processes
usually make extensive use of sophisticated computer vision and computer
graphics tools. At the encoder, the image sequence is initially segmented into
a number of objects. Each object is then analyzed to decide its location, shape,
and texture. The encoder then uses this analysis data to deform a general model
to synthesize an approximation of the object. The same analysis data is also
transmitted to the decoder to synthesize a similar approximation. When the
object starts moving, tracking techniques are used, at the encoder, to estimate
the associated animation data, which is then transmitted to the decoder to
animate the same object. While animation data is suGcient for low quality
reproduction at low bit rates, residual data can also be transmitted to achieve
higher quality reproduction, but at the expense of a higher bit rate. Thus,
once the whole scene is synthesized, only a few animation parameters and
possibly some texture information need to be encoded. Hence, model-based