Page 75 - Video Coding for Mobile Communications Efficiency, Complexity, and Resilience
P. 75
52 Chapter 3. Video Coding: Standards
predicted, respectively. Motion vectors are restricted such that all pels ref-
erenced by them are within the reference picture area. The standard does
not explicitly specify an ME method. However, this MB-based structure im-
plicitly supports block-based approaches and in particular the BMME
algorithm.
3.4.3.4 Motion Vector Coding
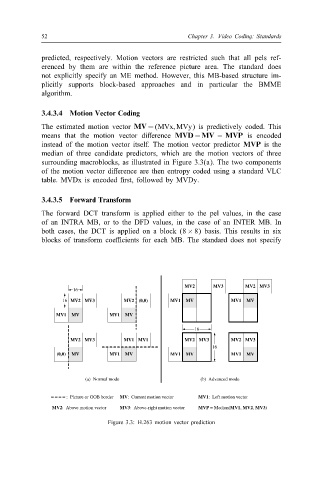
The estimated motion vector MV = (MVx; MVy) is predictively coded. This
means that the motion vector di1erence MVD = MV − MVP is encoded
instead of the motion vector itself. The motion vector predictor MVP is the
median of three candidate predictors, which are the motion vectors of three
surrounding macroblocks, as illustrated in Figure 3.3(a). The two components
of the motion vector di1erence are then entropy coded using a standard VLC
table. MVDx is encoded /rst, followed by MVDy.
3.4.3.5 Forward Transform
The forward DCT transform is applied either to the pel values, in the case
of an INTRA MB, or to the DFD values, in the case of an INTER MB. In
both cases, the DCT is applied on a block (8 × 8) basis. This results in six
blocks of transform coe,cients for each MB. The standard does not specify
MV2 MV3 MV2 MV3
16
16 MV2 MV3 MV2 (0,0) MV1 MV MV1 MV
MV1 MV MV1 MV
16
MV2 MV3 MV1 MV1 MV2 MV3 MV2 MV3
16
(0,0) MV MV1 MV MV1 MV MV1 MV
(a) Normal mode (b) Advanced mode
: Picture or GOB border MV: Current motion vector MV1: Left motion vector
MV2: Above motion vector MV3: Above-right motion vector MVP = Median(MV1, MV2, MV3)
Figure 3.3: H.263 motion vector prediction