Page 21 - Volcanic Textures A Guide To The Interpretation of Textures In Volcanic Rocks
P. 21
computer applications and are not suitable for textural phenocryst size and abundance, and are used for both
analysis and volcanological interpretation. coherent facies and juvenile, essentially monomict
clastic facies. Texture symbols represent the appearance
The format for graphic logs is simple: the vertical axis of the volcanic units, including different sorts of
indicates the depth or thickness and the horizontal axis components, their distribution and approximate relative
shows the average grain size. Adjacent space is used for abundance. Massive coherent lavas and intrusions can
recording younging direction indicators, measurements be portrayed just by composition symbols. Juvenile
of structures, maximum particle size, sampling clast-rich volcaniclastic deposits and lava- or intrusion-
information and a succinct lithological description. related in situ breccia can be shown by combinations of
Ordinary field notebooks and standard logging forms composition and texture symbols. Many texture
can both be adapted to this format (Figs 7, 8). Symbols symbols also imply grain size, as they do in
(Fig. 9) are used on graphic logs to convey two sorts of sedimentological logs. The symbols for sedimentary
information: composition and texture. Composition structures and for non-volcanic sedimentary rocks are
symbols represent interpreted chemical composition, those commonly used in sedimentology.
GRAIN SIZE VOLCANICLASTIC AUTOCLASTIC DEPOSITS RESEDIMENTED
DEPOSITS IN AUTOCLASTIC DEPOSITS
GENERAL and
VOLCANOGENIC
SEDIMENTARY
DEPOSITS
Hyaloclastite Autobreccia Mixture or uncertain
origin
< 1/16 mm volcanic mudstone fine hyaloclastite ? autoclastic mudstone resedimented fine
hyaloclastite, resedimented
autoclastic mudstone
1/1 6-2 mm volcanic sandstone hyaloclastite autoclastic resedimented hyaloclastite
sandstone sandstone sandstone, resedimented
autoclastic sandstone
2-4 mm volcanic granular hyaloclastite granular granular autoclastic resedimented granular
conglomerate, autobreccia breccia hyaloclastite, resedimented
volcanic breccia granular autobreccia,
resedimented granular
autoclastic breccia
4-64 mm hyaloclastite breccia autobreccia autoclastic breccia resedimented hyaloclastite
breccia, resedimented
autobreccia, resedimented
autoclastic breccia
>64mm coarse hyaloclastite coarse coarse autoclastic resedimented coarse
breccia autobreccia breccia hyaloclastite breccia,
resedimented coarse
autobreccia, resedimented
coarse autoclastic breccia
GRAIN SIZE PYROCLASTIC DEPOSITS PYROCLAST-RICH DEPOSITS
Unconsolidated Consolidated RESEDIMENTED SYN-ERUPTIVE Post-eruptive
tephra pyroclastic rock resedimented or reworked,
or uncertain origin
< 1/16 mm fine ash fine tuff resedimented ash-rich mudstone tuffaceous mudstone
1/1 6-2 mm coarse ash coarse tuff resedimented ash-rich sandstone tuffaceous sandstone
2-64 mm lapilli tephra lapillistone (or lapilli resedimented pyroclast-rich tuffaceous conglomerate,
tuff or tuff-breccia) lapillistone, resedimented pumice tuffaceous breccia
lapillistone, resedimented pumice and
lithic lapillistone
> 64mm bomb (fluidal shape) agglomerate (bombs resedimented pyroclast-rich breccia,
tephra, block present), pyroclastic resedimented pumice breccia,
(angular) tephra breccia resedimented pumice and lithic
breccia
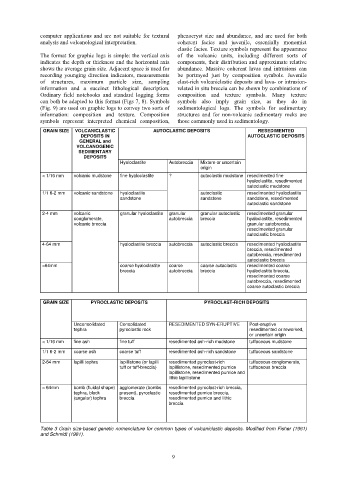
Table 3 Grain size-based genetic nomenclature for common types of volcaniclastic deposits. Modified from Fisher (1961)
and Schmidt (1981).
9