Page 63 - Volcanic Textures A Guide To The Interpretation of Textures In Volcanic Rocks
P. 63
remaining unfragmented (Fig. 20; 13.7). This fragmentation. Complex gradational relationships may
hyaloclastite is unstratified, strictly monomict, and exist between resedimented hyaloclastite, in situ
characterized by jigsaw-fit of clasts (11.6-7), hyaloclastite, coherent lava and feeder dykes, especially
gradational contacts with coherent lava (11.2-3, 11.5), close to the source.
and polyhedral blocky or splintery clasts bounded by
curviplanar surfaces (11.4, 12.1). Clasts are (or were) Intrusive hyaloclastite is typically a texturally complex
entirely or partly glassy and can be vesicular or non- mixture of clasts derived from the intrusion and matrix
vesicular. In many examples of silicic and andesitic derived from the host sediment. Clasts that initially
hyaloclastite the glass is perlitic (12.5), and flow show jigsaw-fit texture can be progressively rotated and
foliations in the parent lava can sometimes be traced separated by narrow seams of host sediment, or else be
continuously from clast to clast in adjacent in situ more widely dispersed in the sediment matrix.
hyaloclastite (Fig. 21; 11.2-3, 11.5). However, intrusive hyaloclastite is essentially in situ,
and only in exceptional circumstances becomes
In situ hyaloclastite may be disturbed by continued involved in resedimentation.
movement of the more ductile interior lava, by flowage
over steep slopes or by intrusions of magma into the On the basis of field studies of submarine volcanic
hyaloclastite pile or by seismic activity. Disturbance sequences of southwest Hokkaido, Yamagishi (1979,
produces results that vary from slight modification of 1987) recognized two types of hyaloclastite with
the jigsaw-fit fabric by rotation and separation of clasts contrasting clast morphologies, interpreted to reflect
to wholesale gravitational collapse and resedimentation. differing magma viscosity at the time of fragmentation.
Mass-flow resedimentation of hyaloclastite by grain- Hyaloclastite (A) is derived from relatively low
flow or density-modified grain-flow processes (Part 4) viscosity magma (basalt, basaltic andesite), occurs in
generates bedded monomict resedimented hyaloclastite close association with pillow lavas, and comprises
breccia. Separate beds can be ungraded or graded massive, monomict breccia composed of pillow
(normal or reverse) and have appreciable primary dips. fragments and isolated pillows dispersed in a finer
Some resedimented hyaloclastite sequences display a matrix (pillow fragment breccia) (15.4, 17.1). The
lateral decrease in grain size with distance from the matrix consists of millimeter- to centimeter-sized,
source (e.g. Dimroth et al., 1978). Although the jigsaw- glassy, splintery or blocky particles with curviplanar
fit fabric is lost, clasts in resedimented hyaloclastite surfaces, produced by spalling of the quenched rims of
usually retain shapes characteristic of quench disintegrating pillows. Similar hyaloclastite-pillow lava
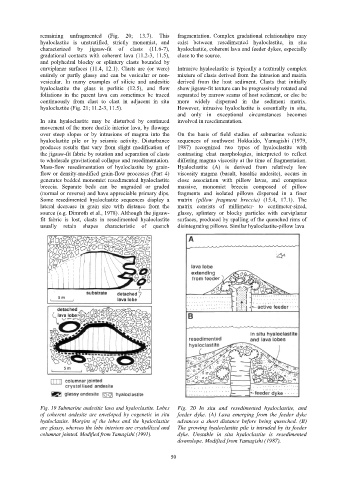
Fig. 19 Submarine andesitic lava and hyaloclastite. Lobes Fig. 20 In situ and resedimented hyaloclastite, and
of coherent andesite are enveloped by cogenetic in situ feeder dyke. (A) Lava emerging from the feeder dyke
hyaloclastite. Margins of the lobes and the hyaloclastite advances a short distance before being quenched. (B)
are glassy, whereas the lobe interiors are crystallized and The growing hyaloclastite pile is intruded by its feeder
columnar jointed. Modified from Yamagishi (1991). dyke. Unstable in situ hyaloclastite is resedimented
downslope. Modified from Yamagishi (1987).
50