Page 424 - Water and Wastewater Engineering Design Principles and Practice
P. 424
SEDIMENTATION 10-41
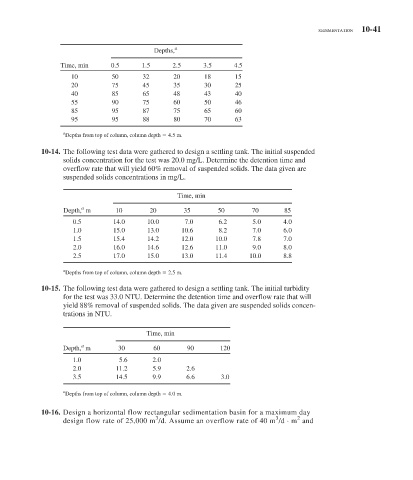
a
Depths,
Time, min 0.5 1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5
10 50 32 20 18 15
20 75 45 35 30 25
40 85 65 48 43 40
55 90 75 60 50 46
85 95 87 75 65 60
95 95 88 80 70 63
a
Depths from top of column, column depth 4.5 m.
10-14. The following test data were gathered to design a settling tank. The initial suspended
solids concentration for the test was 20.0 mg/L. Determine the detention time and
overflow rate that will yield 60% removal of suspended solids. The data given are
suspended solids concentrations in mg/L.
Time, min
a
Depth, m 10 20 35 50 70 85
0.5 14.0 10.0 7.0 6.2 5.0 4.0
1.0 15.0 13.0 10.6 8.2 7.0 6.0
1.5 15.4 14.2 12.0 10.0 7.8 7.0
2.0 16.0 14.6 12.6 11.0 9.0 8.0
2.5 17.0 15.0 13.0 11.4 10.0 8.8
a
Depths from top of column, column depth 2.5 m.
10-15. The following test data were gathered to design a settling tank. The initial turbidity
for the test was 33.0 NTU. Determine the detention time and overflow rate that will
yield 88% removal of suspended solids. The data given are suspended solids concen-
trations in NTU.
Time, min
a
Depth, m 30 60 90 120
1.0 5.6 2.0
2.0 11.2 5.9 2.6
3.5 14.5 9.9 6.6 3.0
a
Depths from top of column, column depth 4.0 m.
10-16. Design a horizontal flow rectangular sedimentation basin for a maximum day
3 3 2
design flow rate of 25,000 m /d. Assume an overflow rate of 40 m /d · m and