Page 187 - Well Control for Completions and Interventions
P. 187
Well Control Surface Equipment 179
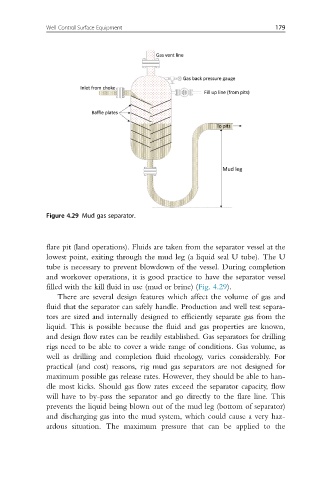
Figure 4.29 Mud gas separator.
flare pit (land operations). Fluids are taken from the separator vessel at the
lowest point, exiting through the mud leg (a liquid seal U tube). The U
tube is necessary to prevent blowdown of the vessel. During completion
and workover operations, it is good practice to have the separator vessel
filled with the kill fluid in use (mud or brine) (Fig. 4.29).
There are several design features which affect the volume of gas and
fluid that the separator can safely handle. Production and well test separa-
tors are sized and internally designed to efficiently separate gas from the
liquid. This is possible because the fluid and gas properties are known,
and design flow rates can be readily established. Gas separators for drilling
rigs need to be able to cover a wide range of conditions. Gas volume, as
well as drilling and completion fluid rheology, varies considerably. For
practical (and cost) reasons, rig mud gas separators are not designed for
maximum possible gas release rates. However, they should be able to han-
dle most kicks. Should gas flow rates exceed the separator capacity, flow
will have to by-pass the separator and go directly to the flare line. This
prevents the liquid being blown out of the mud leg (bottom of separator)
and discharging gas into the mud system, which could cause a very haz-
ardous situation. The maximum pressure that can be applied to the