Page 56 - Well Control for Completions and Interventions
P. 56
Introduction and Well Control Fundamentals 47
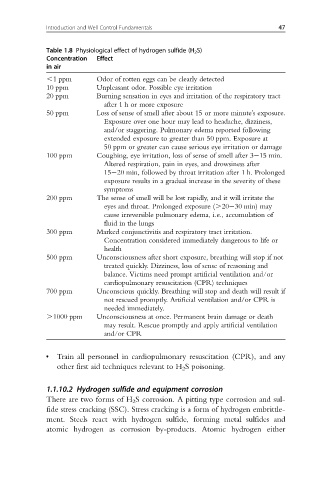
Table 1.8 Physiological effect of hydrogen sulfide (H 2 S)
Concentration Effect
in air
,1 ppm Odor of rotten eggs can be clearly detected
10 ppm Unpleasant odor. Possible eye irritation
20 ppm Burning sensation in eyes and irritation of the respiratory tract
after 1 h or more exposure
50 ppm Loss of sense of smell after about 15 or more minute’s exposure.
Exposure over one hour may lead to headache, dizziness,
and/or staggering. Pulmonary edema reported following
extended exposure to greater than 50 ppm. Exposure at
50 ppm or greater can cause serious eye irritation or damage
100 ppm Coughing, eye irritation, loss of sense of smell after 3 15 min.
Altered respiration, pain in eyes, and drowsiness after
15 20 min, followed by throat irritation after 1 h. Prolonged
exposure results in a gradual increase in the severity of these
symptoms
200 ppm The sense of smell will be lost rapidly, and it will irritate the
eyes and throat. Prolonged exposure (.20 30 min) may
cause irreversible pulmonary edema, i.e., accumulation of
fluid in the lungs
300 ppm Marked conjunctivitis and respiratory tract irritation.
Concentration considered immediately dangerous to life or
health
500 ppm Unconsciousness after short exposure, breathing will stop if not
treated quickly. Dizziness, loss of sense of reasoning and
balance. Victims need prompt artificial ventilation and/or
cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) techniques
700 ppm Unconscious quickly. Breathing will stop and death will result if
not rescued promptly. Artificial ventilation and/or CPR is
needed immediately.
.1000 ppm Unconsciousness at once. Permanent brain damage or death
may result. Rescue promptly and apply artificial ventilation
and/or CPR
• Train all personnel in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), and any
other first aid techniques relevant to H 2 S poisoning.
1.1.10.2 Hydrogen sulfide and equipment corrosion
There are two forms of H 2 S corrosion. A pitting type corrosion and sul-
fide stress cracking (SSC). Stress cracking is a form of hydrogen embrittle-
ment. Steels react with hydrogen sulfide, forming metal sulfides and
atomic hydrogen as corrosion by-products. Atomic hydrogen either