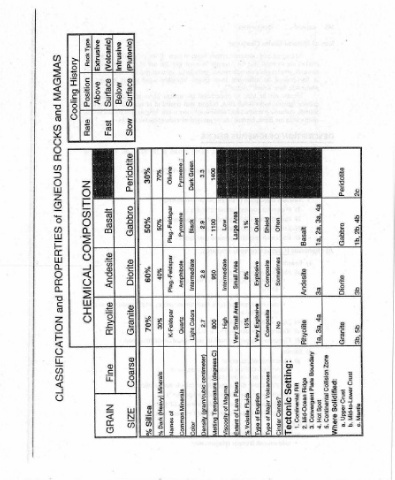
Page 363 - Whole Earth Geophysics An Introductory Textbook For Geologists And Geophysicists
P. 363
AZIs
anueyy “o
9 qb a2 OL
SMUD JOMO7-0}-PIW “4
aWOopusg sg saddp ‘e
:PaljIP'HOS
@UOZ UOISII|OD JeEJUEUNUDD “Ss
yods 10H “p
Asepunog aieig juebseAu0D ‘€
ewjoAyy abpiy Ues90-PIW “Z
yly feueunuoy “4
Bulnjes 914U0}998
SOWIOWOS
SBOUBIIO/A
S|NOJOA
eoly JEWS Rely [JEWS A SMO} BAB] JO
OyeIPSWISIV]
uaealdh weg eyeIPEWE}U]
S|RJOUIN
sedspje4-"Bejg sedspje4-"6eiq sedspje4-y
(o1uesjoq)}| BOeUNS | MOIS S}JOPH8d oiqqey oyUsepuy a}}OA4Y asieog NIVYD
aoIg
eyuels
(Qiuoynid)|
SAISNA}U]
mMojeg
yeseg
oul4
sOeNS
sey
enisnyxyg|
sAOdY
ayey
edA} yooy
UONISOd
NOILISOdWOD IVOINSHO
Asoysipy} Buyooo
SVWSVW pue SyOOH SNOANDI JO SSILHAdOUd PUB NOILVOIsISSVT9
according rock seven compositions the of between the An Common orthoclase or (NaAISi,Os); Common [hornblende, feldspar magma. As liquid. more is, sluggishly, of rivers those than are content minerals tend to to white silica, they magne- black or
of igneous rocks size). The have shown. Properties gradations common window glass. formula SiO,). quartz; feldspar K(Mg,Fe);Si;0,9(OH),]. amphibole plagioclase properties of still is magma (that viscous flow to tend or fountains temperatures high silica determines the silica minerals pink a have in low are iron in high and green, dark
Properties Tectonic classification of texture (grain rocks commonly percentages them exhibit also that makes (chemical include: silica in plagioclase sodium are silica ((Mg,Fe),SiO,]; calcium factor the in molecules the while the more magma thus silica in like freely, more melting lower magmas melt, with silica of properties. High formed therefore rocks When are that
€ Rocks: and illustrates page the composition) and because igneous heavy and mineral magmas form that (0), oxygen stuff the pure is quartz is silica rocks high are that (KAISi,O,); or albite KAI,Si;O ,9(OH),; biotite, low rocks in olivine (Ca,Fe,Mg-Silicate). an is important begins form to tends make to molasses. high Magmas silica flow content to tend
APPENDIX. Igneous Classification, Magmas, Occurrence CLASSIFICATION CHART The next the on chart to content tchemical silica names rough a are guide between falling silica the rocks igneous the and types rock shown. (SiO,)-* Silica Content Silica (Si) silicon is and mineral a of example that found minerals igneous in feldspar potassium (muscovite, micas and minerals igneous in N