Page 293 - Characterization and Properties of Petroleum Fractions - M.R. Riazi
P. 293
QC: —/—
P2: KVU/KXT
P1: KVU/KXT
AT029-06
20:46
AT029-Manual-v7.cls
June 22, 2007
AT029-Manual
Pressure, PSIA
6 7 8 9 10,000
6 7 8 9100
10 T1: IML 30 6. THERMODYNAMIC RELATIONS FOR PROPERTY ESTIMATIONS 273
4 50
6 7 8 91,000
3,000
4 500
300
4
2
2
2
100 100
9 9
8 8
7 7
6 6
5 5
4 4
3 3
2 2
10 10
9 9
8 8
7 Temperature °F 7
6 500 6
5 400 5
4 300 4
3 3
2 200 2
1.0 1.0
9 100 9
8 8
7 80 7
6 6
5 60 5
4 40 4
K = y K = y
/x 3 20 3 /x
0
2 2
0.1 –20 0.1
9 –40 9
8 8
7 7
6 6
5 5
4 4
3 3
2 2
.01 .01
9 9
8 8
7 7
6 6
5 5
4 4
3 3
2 2
.001 .001
10 2 30 4 50 6 7 8 9 100 2 300 4 500 6 7 8 9 1,000 2 3,000 4 6 7 8 9 10,000
Pressure, PSIA Propane
CONV. PRESS. 10,000 PSIA
◦
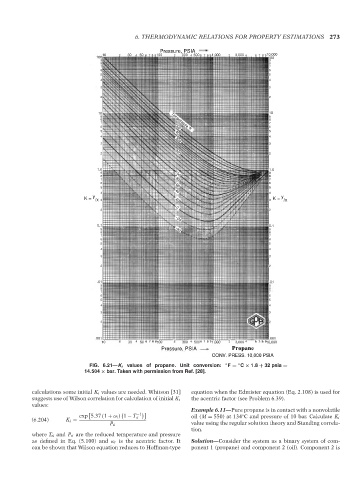
FIG. 6.21—K i values of propane. Unit conversion: ◦ F = C × 1.8 + 32 psia =
14.504 × bar. Taken with permission from Ref. [28].
calculations some initial K i values are needed. Whitson [31] equation when the Edmister equation (Eq. 2.108) is used for
suggests use of Wilson correlation for calculation of initial K i the acentric factor (see Problem 6.39).
values:
Example 6.11—Pure propane is in contact with a nonvolatile
exp 5.37 (1 + ω i) 1 − T ri −1 ◦
(6.204) K i = oil (M = 550) at 134 C and pressure of 10 bar. Calculate K i
P ri value using the regular solution theory and Standing correla-
tion.
where T ri and P ri are the reduced temperature and pressure
as defined in Eq. (5.100) and ω i is the acentric factor. It Solution—Consider the system as a binary system of com-
can be shown that Wilson equation reduces to Hoffman-type ponent 1 (propane) and component 2 (oil). Component 2 is
Copyright ASTM International
Provided by IHS Markit under license with ASTM Licensee=International Dealers Demo/2222333001, User=Anggiansah, Erick
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS Not for Resale, 08/26/2021 21:56:35 MDT
--`,```,`,``````,`,````,```,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---