Page 46 - Characterization and Properties of Petroleum Fractions - M.R. Riazi
P. 46
T1: IML
QC: IML/FFX
P2: IML/FFX
P1: IML/FFX
June 22, 2007
AT029-Manual
AT029-Manual-v7.cls
14:26
AT029-01
26 CHARACTERIZATION AND PROPERTIES OF PETROLEUM FRACTIONS
1.8 PROBLEMS
Europe, Africa, Middle East, Eastern Europe and
Former Soviet Union, and Asia Pacific)?
1.1. State one theory for the formation of petroleum and give b. Where is the location of the biggest refinery in the
names of the hydrocarbon groups in a crude oil. What world and what is its capacity in bbl/d?
are the most important heteroatoms and their concen- c. What is the history of the rate of production of gaso-
tration level in a crude oil? line, distillate, and residual from refineries in the
1.2. The following compounds are generally found in the world and the United States for the last decade?
analysis of a crude oil: ethane, propane, isobutane, 1.9. Characteristics of three reservoir fluids are given below.
n-butane, isopentane, n-pentane, 2,2-dimethylbutane, For each case determine the type of the reservoir fluid
cyclopentane, cyclohexane, n-hexane, 2-methylpentane, using the rule of thumb.
3-methylpentane, benzene, methylcyclopentane, 1,1- a. GOR = 20 scf/stb
dimethylcyclopentane, and hydrocarbons from C 7 and b. GOR = 150 000 scf/stb
heavier grouped as C 7+ . c. CH 4 mol% = 70, API gravity of STO = 40
a. For each compound, draw the chemical structure and 1.10. GOR of a reservoir fluid is 800 scf/stb. Assume the molec-
give the formula. Also indicate the name of hydrocar- ular weight of the stock tank oil is 260 and its specific
bon group that each compound belongs to. gravity is 0.87.
3
3
b. From the above list give the compounds that possibly a. Calculate the GOR in sm /stm and the mole fraction
exist in a gasoline fraction. of gases in the fluid.
1.3. Give the names of n-C 20 , n-C 30 , n-C 40 , and three isomers b. Derive a general mathematical relation to calculate
of n-heptane according to the IUPAC system. GOR from mole fraction of dissolved gas (x A ) through
1.4. List the 10 most important physical properties of crude STO gravity (SG) and oil molecular weight (M).
and its products that are required in both the design and Calculate x A using the developed relation.
operation of an atmospheric distillation column. 1.11. The total LPG production in 1995 was 160 million
1.5. What thermodynamic and physical properties of gas tons/year. If the specific gravity of the liquid is assumed
and/or liquid fluids are required for the following two to be 0.55, what is the production rate in bbl/d?
cases? 1.12. A C 7+ fraction of a crude oil has the following composi-
a. Design and operation of an absorption column with tion in wt%. The molecular weight and specific gravity of
chemical reaction [40, 89]. each pseudocomponent are also given below. Calculate
b. Reservoir simulation [37]. the composition of crude in terms of vol% and mol%.
1.6. What is the characterization of petroleum fractions,
crude oils, and reservoir fluids? Explain their differ- Pseudocomponent wt% M SG
ences. C 7+ (1) 17.3 110 0.750
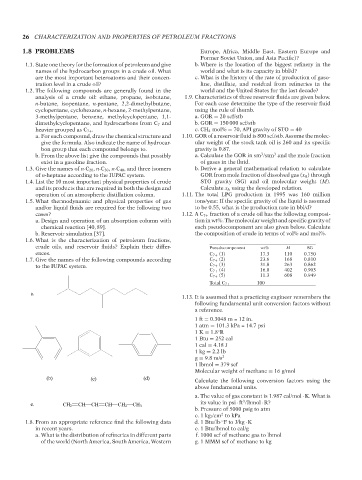
1.7. Give the names of the following compounds according C 7+ (2) 23.6 168 0.810
to the IUPAC system. C 7+ (3) 31.8 263 0.862
C 7+ (4) 16.0 402 0.903
C 7+ (5) 11.3 608 0.949
100
Total C 7+
a.
1.13. It is assumed that a practicing engineer remembers the
following fundamental unit conversion factors without
a reference.
1ft = 0.3048 m = 12 in.
1 atm = 101.3 kPa = 14.7 psi
1K = 1.8 R
◦
1 Btu = 252 cal
1 cal = 4.18 J
1kg = 2.2 lb
g = 9.8 m/s 2
1 lbmol = 379 scf
Molecular weight of methane = 16 g/mol
(b) (c) (d) Calculate the following conversion factors using the
above fundamental units.
a. The value of gas constant is 1.987 cal/mol · K. What is
3
⎯
⎯
⎯
e. CH 2⎯ CH⎯CH CH⎯CH 2 ⎯CH 3 its value in psi · ft /lbmol · R?
b. Pressure of 5000 psig to atm
2
c. 1 kg f /cm to kPa
1.8. From an appropriate reference find the following data d. 1 Btu/lb· F to J/kg · K
◦
in recent years. e. 1 Btu/lbmol to cal/g
a. What is the distribution of refineries in different parts f. 1000 scf of methane gas to lbmol
of the world (North America, South America, Western g. 1 MMM scf of methane to kg
--`,```,`,``````,`,````,```,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
Copyright ASTM International
Provided by IHS Markit under license with ASTM Licensee=International Dealers Demo/2222333001, User=Anggiansah, Erick
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS Not for Resale, 08/26/2021 21:56:35 MDT