Page 227 - Mechanical Behavior of Materials
P. 227
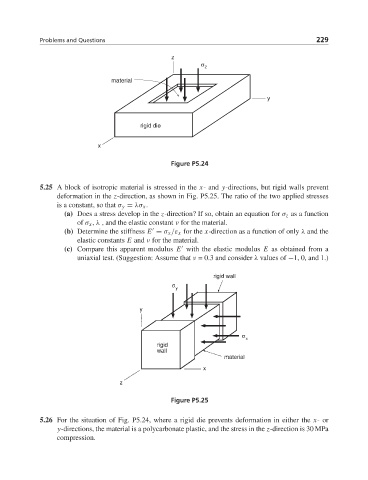
Problems and Questions 229
z
σ z
material
y
rigid die
x
Figure P5.24
5.25 A block of isotropic material is stressed in the x- and y-directions, but rigid walls prevent
deformation in the z-direction, as shown in Fig. P5.25. The ratio of the two applied stresses
is a constant, so that σ y = λσ x .
(a) Does a stress develop in the z-direction? If so, obtain an equation for σ z as a function
of σ x , λ , and the elastic constant ν for the material.
(b) Determine the stiffness E = σ x /ε x for the x-direction as a function of only λ and the
elastic constants E and ν for the material.
(c) Compare this apparent modulus E with the elastic modulus E as obtained from a
uniaxial test. (Suggestion: Assume that ν =0.3 and consider λ values of −1, 0, and 1.)
Figure P5.25
5.26 For the situation of Fig. P5.24, where a rigid die prevents deformation in either the x-or
y-directions, the material is a polycarbonate plastic, and the stress in the z-direction is 30 MPa
compression.