Page 88 - Mechanical Behavior of Materials
P. 88
Section 3.5 Polymers 89
Figure 3.14 Polymer chain structures that are (a) linear, (b) branched, or (c) cross-linked.
(From [Budinski 96] pp. 63–64; c 1996 by Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ; reprinted
with permission.)
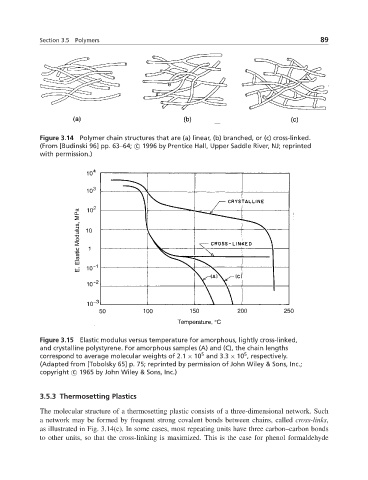
Figure 3.15 Elastic modulus versus temperature for amorphous, lightly cross-linked,
and crystalline polystyrene. For amorphous samples (A) and (C), the chain lengths
5
5
correspond to average molecular weights of 2.1 × 10 and 3.3 × 10 , respectively.
(Adapted from [Tobolsky 65] p. 75; reprinted by permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc.;
copyright c 1965 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.)
3.5.3 Thermosetting Plastics
The molecular structure of a thermosetting plastic consists of a three-dimensional network. Such
a network may be formed by frequent strong covalent bonds between chains, called cross-links,
as illustrated in Fig. 3.14(c). In some cases, most repeating units have three carbon–carbon bonds
to other units, so that the cross-linking is maximized. This is the case for phenol formaldehyde