Page 125 - Algae Anatomy, Biochemistry, and Biotechnology
P. 125
108 Algae: Anatomy, Biochemistry, and Biotechnology
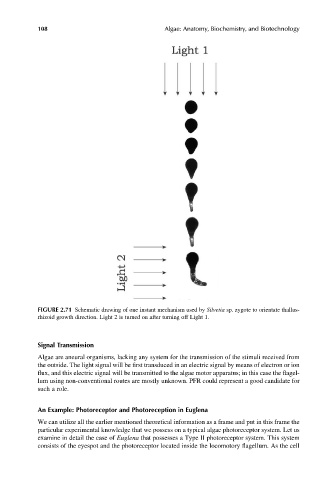
FIGURE 2.71 Schematic drawing of one instant mechanism used by Silvetia sp. zygote to orientate thallus-
rhizoid growth direction. Light 2 is turned on after turning off Light 1.
Signal Transmission
Algae are aneural organisms, lacking any system for the transmission of the stimuli received from
the outside. The light signal will be first transduced in an electric signal by means of electron or ion
flux, and this electric signal will be transmitted to the algae motor apparatus; in this case the flagel-
lum using non-conventional routes are mostly unknown. PFR could represent a good candidate for
such a role.
An Example: Photoreceptor and Photoreception in Euglena
We can utilize all the earlier mentioned theoretical information as a frame and put in this frame the
particular experimental knowledge that we possess on a typical algae photoreceptor system. Let us
examine in detail the case of Euglena that possesses a Type II photoreceptor system. This system
consists of the eyespot and the photoreceptor located inside the locomotory flagellum. As the cell