Page 170 - Algae Anatomy, Biochemistry, and Biotechnology
P. 170
Photosynthesis 153
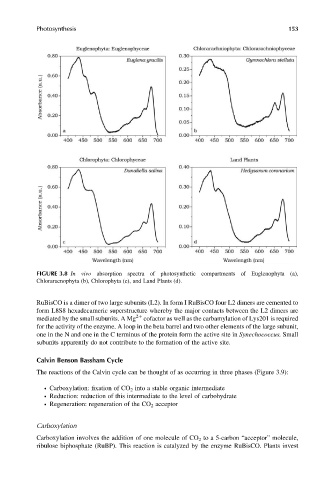
FIGURE 3.8 In vivo absorption spectra of photosynthetic compartments of Euglenophyta (a),
Chloraracnophyta (b), Chlorophyta (c), and Land Plants (d).
RuBisCO is a dimer of two large subunits (L2). In form I RuBisCO four L2 dimers are cemented to
form L8S8 hexadecameric superstructure whereby the major contacts between the L2 dimers are
mediated by the small subunits. A Mg 2þ cofactor as well as the carbamylation of Lys201 is required
for the activity of the enzyme. A loop in the beta barrel and two other elements of the large subunit,
one in the N and one in the C terminus of the protein form the active site in Synechococcus. Small
subunits apparently do not contribute to the formation of the active site.
Calvin Benson Bassham Cycle
The reactions of the Calvin cycle can be thought of as occurring in three phases (Figure 3.9):
. Carboxylation: fixation of CO 2 into a stable organic intermediate
. Reduction: reduction of this intermediate to the level of carbohydrate
. Regeneration: regeneration of the CO 2 acceptor
Carboxylation
Carboxylation involves the addition of one molecule of CO 2 to a 5-carbon “acceptor” molecule,
ribulose biphosphate (RuBP). This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme RuBisCO. Plants invest