Page 96 - Algae Anatomy, Biochemistry, and Biotechnology
P. 96
Anatomy 79
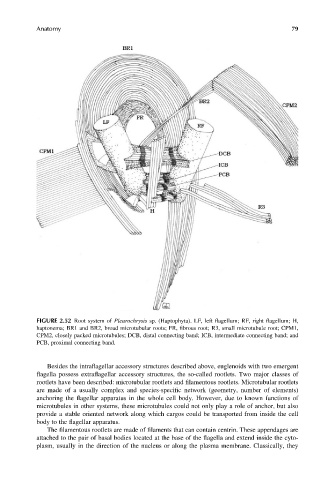
FIGURE 2.52 Root system of Pleurochrysis sp. (Haptophyta). LF, left flagellum; RF, right flagellum; H,
haptonema; BR1 and BR2, broad microtubular roots; FR, fibrous root; R3, small microtubule root; CPM1,
CPM2, closely packed microtubules; DCB, distal connecting band; ICB, intermediate connecting band; and
PCB, proximal connecting band.
Besides the intraflagellar accessory structures described above, euglenoids with two emergent
flagella possess extraflagellar accessory structures, the so-called rootlets. Two major classes of
rootlets have been described: microtubular rootlets and filamentous rootlets. Microtubular rootlets
are made of a usually complex and species-specific network (geometry, number of elements)
anchoring the flagellar apparatus in the whole cell body. However, due to known functions of
microtubules in other systems, these microtubules could not only play a role of anchor, but also
provide a stable oriented network along which cargos could be transported from inside the cell
body to the flagellar apparatus.
The filamentous rootlets are made of filaments that can contain centrin. These appendages are
attached to the pair of basal bodies located at the base of the flagella and extend inside the cyto-
plasm, usually in the direction of the nucleus or along the plasma membrane. Classically, they