Page 99 - Algae Anatomy, Biochemistry, and Biotechnology
P. 99
82 Algae: Anatomy, Biochemistry, and Biotechnology
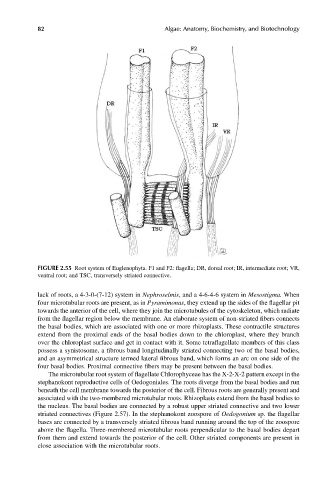
FIGURE 2.55 Root system of Euglenophyta. F1 and F2: flagella; DR, dorsal root; IR, intermediate root; VR,
ventral root; and TSC, transversely striated connective.
lack of roots, a 4-3-0-(7-12) system in Nephroselmis, and a 4-6-4-6 system in Mesostigma. When
four microtubular roots are present, as in Pyramimonas, they extend up the sides of the flagellar pit
towards the anterior of the cell, where they join the microtubules of the cytoskeleton, which radiate
from the flagellar region below the membrane. An elaborate system of non-striated fibers connects
the basal bodies, which are associated with one or more rhizoplasts. These contractile structures
extend from the proximal ends of the basal bodies down to the chloroplast, where they branch
over the chloroplast surface and get in contact with it. Some tetraflagellate members of this class
possess a synistosome, a fibrous band longitudinally striated connecting two of the basal bodies,
and an asymmetrical structure termed lateral fibrous band, which forms an arc on one side of the
four basal bodies. Proximal connective fibers may be present between the basal bodies.
The microtubular root system of flagellate Chlorophyceae has the X-2-X-2 pattern except in the
stephanokont reproductive cells of Oedogoniales. The roots diverge from the basal bodies and run
beneath the cell membrane towards the posterior of the cell. Fibrous roots are generally present and
associated with the two-membered microtubular roots. Rhizoplasts extend from the basal bodies to
the nucleus. The basal bodies are connected by a robust upper striated connective and two lower
striated connectives (Figure 2.57). In the stephanokont zoospore of Oedogonium sp. the flagellar
bases are connected by a transversely striated fibrous band running around the top of the zoospore
above the flagella. Three-membered microtubular roots perpendicular to the basal bodies depart
from them and extend towards the posterior of the cell. Other striated components are present in
close association with the microtubular roots.