Page 114 - Introduction to Marine Engineering
P. 114
Feed systems 101
Economiser
"**~1 1 I* 1
^nF
.« ,jr
-**-
-If- h\
," Boiler
(Condenser} v, 71-
*Alr X Recirculating
and line ' Drains <-<>wP«*sure
vapour Air cooler heat er Superheater
.
ejector
tJu _/
High pressure
heater
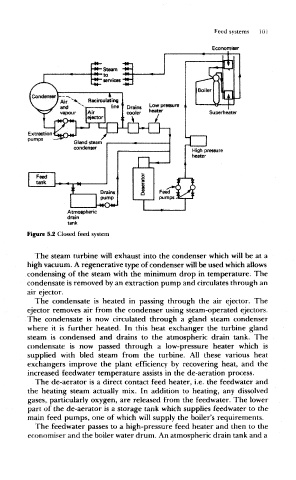
Figure 5.2 Closed feed system
The steam turbine will exhaust into the condenser which will be at a
high vacuum. A regenerative type of condenser will be used which allows
condensing of the steam with the minimum drop in temperature. The
condensate is removed by an extraction pump and circulates through an
air ejector.
The condensate is heated in passing through the air ejector. The
ejector removes air from the condenser using steam-ope rated ejectors.
The condensate is now circulated through a gland steam condenser
where it is further heated. In this heat exchanger the turbine gland
steam is condensed and drains to the atmospheric drain tank. The
condensate is now passed through a low-pressure heater which is
supplied with bled steam from the turbine. All these various heat
exchangers improve the plant efficiency by recovering heat, and the
increased feedwater temperature assists in the de-aeration process.
The de-aerator is a direct contact feed heater, i.e. the feedwater and
the heating steam actually mix. In addition to heating, any dissolved
gases, particularly oxygen, are released from the feedwater. The lower
part of the de-aerator is a storage tank which supplies feedwater to the
main feed pumps, one of which will supply the boiler's requirements.
The feedwater passes to a high-pressure feed heater and then to the
economiser and the boiler water drum. An atmospheric drain tank and a