Page 118 - Introduction to Marine Engineering
P. 118
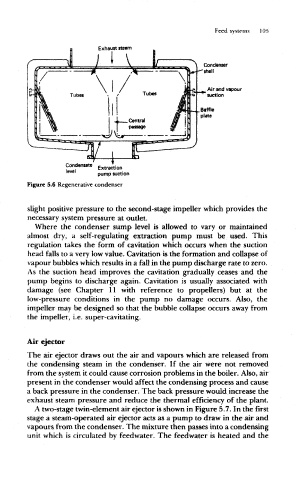
Feed systems 105
Exhaust steam
Condenser
shell
Air and vapour
suction
Extraction
pump suction
Figure 5.6 Regenerative condenser
slight positive pressure to the second-stage impeller which provides the
necessary system pressure at outlet.
Where the condenser sump level is allowed to vary or maintained
almost dry, a self-regulating extraction pump must be used. This
regulation takes the form of cavitation which occurs when the suction
head falls to a very low value. Cavitation is the formation and collapse of
vapour bubbles which results in a fall in the pump discharge rate to zero.
As the suction head improves the cavitation gradually ceases and the
pump begins to discharge again. Cavitation is usually associated with
damage (see Chapter 11 with reference to propellers) but at the
low-pressure conditions in the pump no damage occurs. Also, the
impeller may be designed so that the bubble collapse occurs away from
the impeller, i.e. super-cavitating.
Air ejector
The air ejector draws out the air and vapours which are released from
the condensing steam in the condenser. If the air were not removed
from the system it could cause corrosion problems in the boiler. Also, air
present in the condenser would affect the condensing process and cause
a back pressure in the condenser. The back pressure would increase the
exhaust steam pressure and reduce the thermal efficiency of the plant.
A two-stage twin-element air ejector is shown in Figure 5.7. In the first
stage a steam-operated air ejector acts as a pump to draw in the air and
vapours from the condenser. The mixture then passes into a condensing
unit which is circulated by feedwater. The feedwater is heated and the