Page 120 - Introduction to Marine Engineering
P. 120
Feed systems 107
The gland steam condenser collects steam, vapour and air from the
turbine gland steam system. These returns are cooled by the circulating
feed water and the steam is condensed. The condensate is returned to
the system via a loop seal or some form of steam trap and any air present
Is discharged into the atmosphere. The feedwater passes through
U-tubes within the shell of the unit.
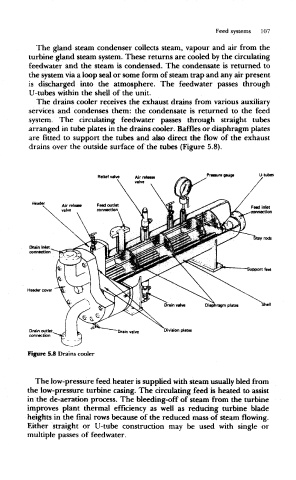
The drains cooler receives the exhaust drains from various auxiliary
services and condenses them: the condensate is returned to the feed
system. The circulating feedwater passes through straight tubes
arranged in tube plates in the drains cooler. Baffles or diaphragm plates
are fitted to support the tubes and also direct the flow of the exhaust
drains over the outside surface of the tubes (Figure 5.8).
Premire gauge U-tubes
Relief valve
Header
Drain valve Diaphragm plates
Division plates
Figure 5.8 Drains cooler
The low-pressure feed heater is supplied with steam usually bled from
the low-pressure turbine casing. The circulating feed is heated to assist
in the de-aeration process. The bleeding-off of steam from the turbine
improves plant thermal efficiency as well as reducing turbine blade
heights in the final rows because of the reduced mass of steam flowing.
Either straight or U-tube construction may be used with single or
multiple passes of feedwater.