Page 207 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 207
4.3 Structure of Impact Assessment according to ISO 14040 and 14044 191
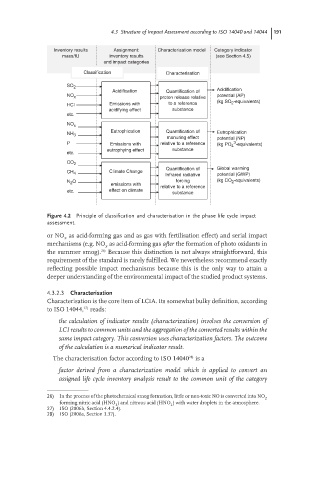
Inventory results Assignment: Characterisation model Category indicator
mass/fU inventory results (see Section 4.5)
and impact categories
Classification Characterisation
SO 2
Acidification Quantification of Acidification
NO x potential (AP)
proton release relative
HCl Emissions with to a reference (kg SO 2 -equivalents)
acidifying effect substance
etc.
NO x
Eutrophication Quantification of Eutrophication
NH 3
manuring effect potential (NP)
3
P Emissions with relative to a reference (kg PO 4 -equivalents)
eutrophying effect substance
etc.
CO 2
Quantification of Global warming
Climate Change
CH 4
Infrared radiative potential (GWP)
N 2 O forcing (kg CO 2 -equivalents)
emissions with relative to a reference
etc. effect on climate substance
Figure 4.2 Principle of classification and characterisation in the phase life cycle impact
assessment.
or NO as acid-forming gas and as gas with fertilisation effect) and serial impact
x
mechanisms (e.g. NO as acid-forming gas after the formation of photo oxidants in
x
the summer smog). 26) Because this distinction is not always straightforward, this
requirement of the standard is rarely fulfilled. We nevertheless recommend exactly
reflecting possible impact mechanisms because this is the only way to attain a
deeper understanding of the environmental impact of the studied product systems.
4.3.2.3 Characterisation
Characterisation is the core item of LCIA. Its somewhat bulky definition, according
to ISO 14044, 27) reads:
the calculation of indicator results (characterization) involves the conversion of
LCI results to common units and the aggregation of the converted results within the
same impact category. This conversion uses characterization factors. The outcome
of the calculation is a numerical indicator result.
The characterisation factor according to ISO 14040 28) is a
factor derived from a characterization model which is applied to convert an
assigned life cycle inventory analysis result to the common unit of the category
26) In the process of the photochemical smog formation, little or non-toxic NO is converted into NO
2
forming nitric acid (HNO ) and nitrous acid (HNO ) with water droplets in the atmosphere.
3 2
27) ISO (2006b, Section 4.4.2.4).
28) ISO (2006a, Section 3.37).