Page 280 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 280
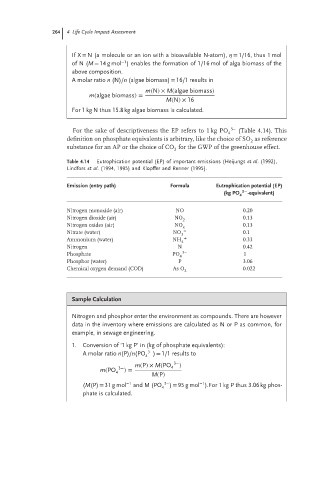
264 4 Life Cycle Impact Assessment
If X = N (a molecule or an ion with a bioavailable N-atom), = 1/16, thus 1 mol
−1
of N (M = 14gmol ) enables the formation of 1/16 mol of alga biomass of the
above composition.
A molar ratio n (N)/n (algae biomass) = 16/1 results in
m(N)× M(algae biomass)
m(algae biomass)=
M(N)× 16
For 1 kg N thus 15.8 kg algae biomass is calculated.
For the sake of descriptiveness the EP refers to 1 kg PO 4 3− (Table 4.14). This
definition on phosphate equivalents is arbitrary, like the choice of SO as reference
2
substance for an AP or the choice of CO for the GWP of the greenhouse effect.
2
Table 4.14 Eutrophication potential (EP) of important emissions (Heijungs et al. (1992),
Lindfors et al. (1994, 1995) and Kl¨ opffer and Renner (1995).
Emission (entry path) Formula Eutrophication potential (EP)
3−
(kg PO -equivalent)
4
Nitrogen monoxide (air) NO 0.20
Nitrogen dioxide (air) NO 0.13
2
Nitrogen oxides (air) NO x 0.13
Nitrate (water) NO − 0.1
3
Ammonium (water) NH 4 + 0.33
Nitrogen N 0.42
Phosphate PO 3− 1
4
Phosphor (water) P 3.06
Chemical oxygen demand (COD) As O 0.022
2
Sample Calculation
Nitrogen and phosphor enter the environment as compounds. There are however
data in the inventory where emissions are calculated as N or P as common, for
example, in sewage engineering.
1. Conversion of ‘1 kg P’ in (kg of phosphate equivalents):
A molar ratio n(P)/n(PO 3– ) = 1/1 results to
4
m(P)× M(PO 4 3− )
3−
m(PO 4 )= M(P)
−1
(M(P) = 31gmol −1 and M (PO 4 3− ) = 95gmol ).For 1 kg P thus 3.06 kg phos-
phate is calculated.