Page 100 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 100
8 Scope Definition 85
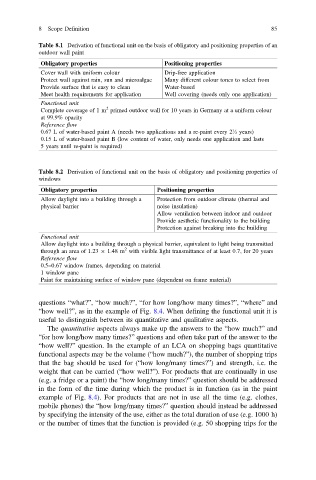
Table 8.1 Derivation of functional unit on the basis of obligatory and positioning properties of an
outdoor wall paint
Obligatory properties Positioning properties
Cover wall with uniform colour Drip-free application
Protect wall against rain, sun and microalgae Many different colour tones to select from
Provide surface that is easy to clean Water-based
Meet health requirements for application Well covering (needs only one application)
Functional unit
2
Complete coverage of 1 m primed outdoor wall for 10 years in Germany at a uniform colour
at 99.9% opacity
Reference flow
0.67 L of water-based paint A (needs two applications and a re-paint every 2½ years)
0.15 L of water-based paint B (low content of water, only needs one application and lasts
5 years until re-paint is required)
Table 8.2 Derivation of functional unit on the basis of obligatory and positioning properties of
windows
Obligatory properties Positioning properties
Allow daylight into a building through a Protection from outdoor climate (thermal and
physical barrier noise insulation)
Allow ventilation between indoor and outdoor
Provide aesthetic functionality to the building
Protection against breaking into the building
Functional unit
Allow daylight into a building through a physical barrier, equivalent to light being transmitted
2
through an area of 1.23 1.48 m with visible light transmittance of at least 0.7, for 20 years
Reference flow
0.5–0.67 window frames, depending on material
1 window pane
Paint for maintaining surface of window pane (dependent on frame material)
questions “what?”, “how much?”, “for how long/how many times?”, “where” and
“how well?”, as in the example of Fig. 8.4. When defining the functional unit it is
useful to distinguish between its quantitative and qualitative aspects.
The quantitative aspects always make up the answers to the “how much?” and
“for how long/how many times?” questions and often take part of the answer to the
“how well?” question. In the example of an LCA on shopping bags quantitative
functional aspects may be the volume (“how much?”), the number of shopping trips
that the bag should be used for (“how long/many times?”) and strength, i.e. the
weight that can be carried (“how well?”). For products that are continually in use
(e.g. a fridge or a paint) the “how long/many times?” question should be addressed
in the form of the time during which the product is in function (as in the paint
example of Fig. 8.4). For products that are not in use all the time (e.g. clothes,
mobile phones) the “how long/many times?” question should instead be addressed
by specifying the intensity of the use, either as the total duration of use (e.g. 1000 h)
or the number of times that the function is provided (e.g. 50 shopping trips for the