Page 220 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 220
206 R.K. Rosenbaum et al.
since then with the latest version in the Fifth Assessment Report (IPCC 2013).
Global warming potentials are calculated for each GHG according to:
R T
0 a i C i ðtÞdt
GWP i ¼ R T ð10:4Þ
0 a CO 2 C CO 2 ðtÞdt
where
• a i : thermal radiation absorption (instant radiative forcing) following an increase
of one unit in the concentration of gas i
• C i (t): Concentration of gas i remaining at time t after emission
• T: number of years for which the integration is carried out (e.g. 20 or 100 years)
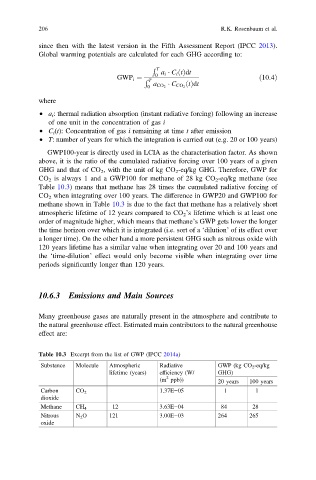
GWP100-year is directly used in LCIA as the characterisation factor. As shown
above, it is the ratio of the cumulated radiative forcing over 100 years of a given
GHG and that of CO 2 , with the unit of kg CO 2 -eq/kg GHG. Therefore, GWP for
CO 2 is always 1 and a GWP100 for methane of 28 kg CO 2 -eq/kg methane (see
Table 10.3) means that methane has 28 times the cumulated radiative forcing of
CO 2 when integrating over 100 years. The difference in GWP20 and GWP100 for
methane shown in Table 10.3 is due to the fact that methane has a relatively short
atmospheric lifetime of 12 years compared to CO 2 ’s lifetime which is at least one
order of magnitude higher, which means that methane’s GWP gets lower the longer
the time horizon over which it is integrated (i.e. sort of a ‘dilution’ of its effect over
a longer time). On the other hand a more persistent GHG such as nitrous oxide with
120 years lifetime has a similar value when integrating over 20 and 100 years and
the ‘time-dilution’ effect would only become visible when integrating over time
periods significantly longer than 120 years.
10.6.3 Emissions and Main Sources
Many greenhouse gases are naturally present in the atmosphere and contribute to
the natural greenhouse effect. Estimated main contributors to the natural greenhouse
effect are:
Table 10.3 Excerpt from the list of GWP (IPCC 2014a)
Substance Molecule Atmospheric Radiative GWP (kg CO 2 -eq/kg
lifetime (years) efficiency (W/ GHG)
2
(m ppb)) 20 years 100 years
Carbon CO 2 1.37E−05 1 1
dioxide
Methane CH 4 12 3.63E−04 84 28
Nitrous N 2 O 121 3.00E−03 264 265
oxide