Page 76 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 76
6 Introduction to LCA Methodology 61
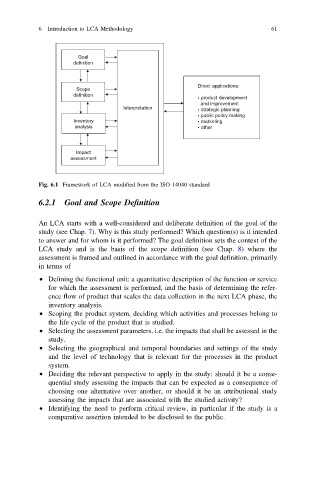
Goal
definition
Direct applications:
Scope
definition
product development
and improvement
Interpretation strategic planning
public policy making
Inventory marketing
analysis other
Impact
assessment
Fig. 6.1 Framework of LCA modified from the ISO 14040 standard
6.2.1 Goal and Scope Definition
An LCA starts with a well-considered and deliberate definition of the goal of the
study (see Chap. 7). Why is this study performed? Which question(s) is it intended
to answer and for whom is it performed? The goal definition sets the context of the
LCA study and is the basis of the scope definition (see Chap. 8) where the
assessment is framed and outlined in accordance with the goal definition, primarily
in terms of
• Defining the functional unit: a quantitative description of the function or service
for which the assessment is performed, and the basis of determining the refer-
ence flow of product that scales the data collection in the next LCA phase, the
inventory analysis.
• Scoping the product system, deciding which activities and processes belong to
the life cycle of the product that is studied.
• Selecting the assessment parameters, i.e. the impacts that shall be assessed in the
study.
• Selecting the geographical and temporal boundaries and settings of the study
and the level of technology that is relevant for the processes in the product
system.
• Deciding the relevant perspective to apply in the study: should it be a conse-
quential study assessing the impacts that can be expected as a consequence of
choosing one alternative over another, or should it be an attributional study
assessing the impacts that are associated with the studied activity?
• Identifying the need to perform critical review, in particular if the study is a
comparative assertion intended to be disclosed to the public.