Page 122 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 122
Textile Wastewater Treatment by Advanced Oxidation Processes 103
TOTAL 505 90 29 624
80%
60%
40%
20%
0%
Azo dyes Carbonyl Phthalocyanine TOTAL
dyes dyes
Photocatalysis H2O2/UV
Ultrasonic cavitation Catalytic O3
Photo-fenton processes H202/O3
H2O2/Fe2+ O3
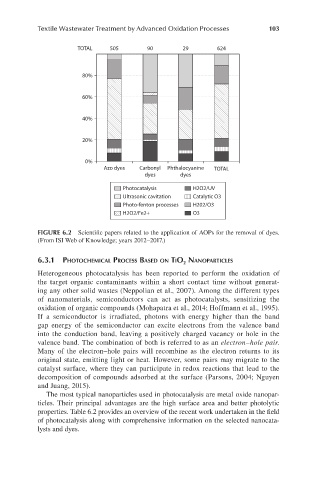
FIGURE 6.2 Scientific papers related to the application of AOPs for the removal of dyes.
(From ISI Web of Knowledge; years 2012–2017.)
6.3.1 pHoTocHeMical process baseD on Tio nanoparTicles
2
Heterogeneous photocatalysis has been reported to perform the oxidation of
the target organic contaminants within a short contact time without generat-
ing any other solid wastes (Neppolian et al., 2007). Among the different types
of nanomaterials, semiconductors can act as photocatalysts, sensitizing the
oxidation of organic compounds (Mohapatra et al., 2014; Hoffmann et al., 1995).
If a semiconductor is irradiated, photons with energy higher than the band
gap energy of the semiconductor can excite electrons from the valence band
into the conduction band, leaving a positively charged vacancy or hole in the
valence band. The combination of both is referred to as an electron–hole pair.
Many of the electron–hole pairs will recombine as the electron returns to its
original state, emitting light or heat. However, some pairs may migrate to the
catalyst surface, where they can participate in redox reactions that lead to the
decomposition of compounds adsorbed at the surface (Parsons, 2004; Nguyen
and Juang, 2015).
The most typical nanoparticles used in photocatalysis are metal oxide nanopar-
ticles. Their principal advantages are the high surface area and better photolytic
properties. Table 6.2 provides an overview of the recent work undertaken in the field
of photocatalysis along with comprehensive information on the selected nanocata-
lysts and dyes.