Page 126 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 126
Textile Wastewater Treatment by Advanced Oxidation Processes 107
6.3.2 HeTerogeneous fenTon caTalyTic DegraDaTion
baseD on MagneTiTe nanoparTicles
The concept of the Fenton process relies on the generation of OH∙ from H O with
2
2
iron ions acting as a homogeneous catalyst in an acidic medium (Bautista et al.,
2008; Fenton, 1894). An overview regarding the application of the heterogeneous
Fenton process for the removal of dyes is provided in Table 6.3.
Beyond these processes, the use of Fe O nanoparticles as a catalyst substituting
3
4
2+
the use of soluble Fe may be a promising technology. The potential of these materi-
als derives from their higher ability for degradation of recalcitrant pollutants com-
pared with conventional iron-supported catalysts due to the presence of both Fe and
2+
3+
Fe species. In addition, their magnetic properties allow their easy, fast, and inex-
pensive separation from the reaction medium (Munoz et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2014).
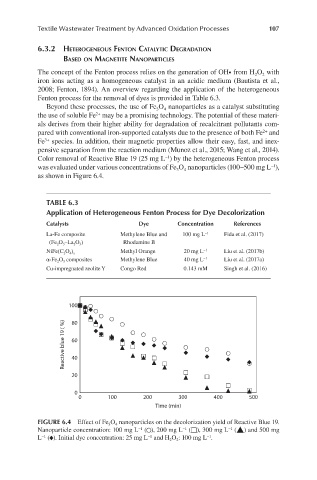
−1
Color removal of Reactive Blue 19 (25 mg L ) by the heterogeneous Fenton process
was evaluated under various concentrations of Fe O nanoparticles (100–500 mg L ),
−1
4
3
as shown in Figure 6.4.
TABLE 6.3
Application of Heterogeneous Fenton Process for Dye Decolorization
Catalysts Dye Concentration References
La-Fe composite Methylene Blue and 100 mg L −1 Fida et al. (2017)
(Fe 2 O 3 –La 2 O 3 ) Rhodamine B
Methyl Orange 20 mg L −1 Liu et al. (2017b)
NiFe(C 2 O 4 ) x
α-Fe 2 O 3 composites Methylene Blue 40 mg L −1 Liu et al. (2017a)
Cu-impregnated zeolite Y Congo Red 0.143 mM Singh et al. (2016)
100
80
Reactive blue 19 ( %) 60
40
20
0
0 100 200 300 400 500
Time (min)
FIGURE 6.4 Effect of Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles on the decolorization yield of Reactive Blue 19.
−1
Nanoparticle concentration: 100 mg L (○), 200 mg L (□), 300 mg L (▲) and 500 mg
−1
−1
−1
L (♦). Initial dye concentration: 25 mg L and H 2 O 2 : 100 mg L .
−1
−1