Page 61 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 61
42 Life Cycle Assessment of Wastewater Treatment
With GHG
Without GHG
0.00 0.15 0.30 0.45 0.60 0.75
3
GWP (kg CO [eq]/m )
2
With GHG
Without GHG
0.00 0.15 0.30 0.45 0.60 0.75
3
GWP (kg CO [eq]/m )
2
Sluge management Sluge line Secondary treatment
Primary treatment Pretreatment
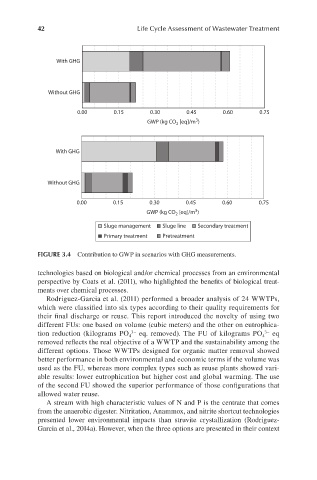
FIGURE 3.4 Contribution to GWP in scenarios with GHG measurements.
technologies based on biological and/or chemical processes from an environmental
perspective by Coats et al. (2011), who highlighted the benefits of biological treat-
ments over chemical processes.
Rodriguez-Garcia et al. (2011) performed a broader analysis of 24 WWTPs,
which were classified into six types according to their quality requirements for
their final discharge or reuse. This report introduced the novelty of using two
different FUs: one based on volume (cubic meters) and the other on eutrophica-
tion reduction (kilograms PO 4 3− eq. removed). The FU of kilograms PO 4 3− eq
removed reflects the real objective of a WWTP and the sustainability among the
different options. Those WWTPs designed for organic matter removal showed
better performance in both environmental and economic terms if the volume was
used as the FU, whereas more complex types such as reuse plants showed vari-
able results: lower eutrophication but higher cost and global warming. The use
of the second FU showed the superior performance of those configurations that
allowed water reuse.
A stream with high characteristic values of N and P is the centrate that comes
from the anaerobic digester. Nitritation, Anammox, and nitrite shortcut technologies
presented lower environmental impacts than struvite crystallization (Rodriguez-
Garcia et al., 2014a). However, when the three options are presented in their context