Page 53 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 53
36 Practical Design Calculations for Groundwater and Soil Remediation
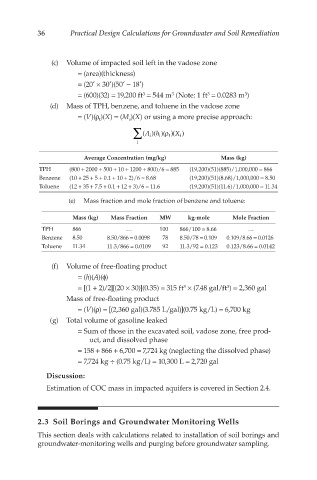
(c) Volume of impacted soil left in the vadose zone
= (area)(thickness)
= (20′ × 30′)(50′ − 18′)
= (600)(32) = 19,200 ft = 544 m (Note: 1 ft = 0.0283 m )
3
3
3
3
(d) Mass of TPH, benzene, and toluene in the vadose zone
= (V)(ρ )(X) = (M )(X) or using a more precise approach:
s
t
∑ (Ah i ρ t i )
)()()(X
i
i
Average Concentration (mg/kg) Mass (kg)
TPH (800 + 2000 + 500 + 10 + 1200 + 800)/6 = 885 (19,200)(51)(885)/1,000,000 = 866
Benzene (10 + 25 + 5 + 0.1 + 10 + 2)/6 = 8.68 (19,200)(51)(8.68)/1,000,000 = 8.50
Toluene (12 + 35 + 7.5 + 0.1 + 12 + 3)/6 = 11.6 (19,200)(51)(11.6)/1,000,000 = 11.34
(e) Mass fraction and mole fraction of benzene and toluene:
Mass (kg) Mass Fraction MW kg-mole Mole Fraction
TPH 866 … 100 866/100 = 8.66 …
Benzene 8.50 8.50/866 = 0.0098 78 8.50/78 = 0.109 0.109/8.66 = 0.0126
Toluene 11.34 11.3/866 = 0.0109 92 11.3/92 = 0.123 0.123/8.66 = 0.0142
(f) Volume of free-floating product
= (h)(A)(ϕ)
= [(1 + 2)/2][(20 × 30)](0.35) = 315 ft × (7.48 gal/ft ) = 2,360 gal
3
3
Mass of free-floating product
= (V)(ρ) = [(2,360 gal)(3.785 L/gal)](0.75 kg/L) = 6,700 kg
(g) Total volume of gasoline leaked
= Sum of those in the excavated soil, vadose zone, free prod-
uct, and dissolved phase
= 158 + 866 + 6,700 = 7,724 kg (neglecting the dissolved phase)
= 7,724 kg ÷ (0.75 kg/L) = 10,300 L = 2,720 gal
Discussion:
Estimation of COC mass in impacted aquifers is covered in Section 2.4.
2.3 Soil Borings and Groundwater Monitoring Wells
This section deals with calculations related to installation of soil borings and
groundwater-monitoring wells and purging before groundwater sampling.