Page 217 - 3D Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
P. 217
206 30 Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
pinned composites is examined based on the limited amount of published data and
information. Included in this chapter is a description of the fabrication techniques, the
in-plane and through-thickness mechanical properties, and impact damage tolerance of
z-pinned composites. 3D sandwich composites manufactured using Z-fiberTM
technology is also briefly described.
9.2 FABRICATION OF Z-PINNED COMPOSITES
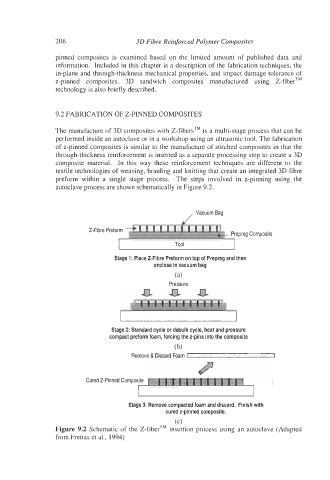
The manufacture of 3D composites with Z-fibersTM is a multi-stage process that can be
performed inside an autoclave or in a workshop using an ultrasonic tool. The fabrication
of z-pinned composites is similar to the manufacture of stitched composites in that the
through-thickness reinforcement is inserted as a separate processing step to create a 3D
composite material. In this way these reinforcement techniques are different to the
textile technologies of weaving, braiding and knitting that create an integrated 3D fibre
preform within a single stage process. The steps involved in z-pinning using the
autoclave process are shown schematically in Figure 9.2.
, VacuumBag
2-Fibre Preform
epreg Composite
Stage 1: Place 2-Fibre Preform on top of Prepreg and then
enclose in vacuum bag
(a)
Pressure
0
Stage 2: Standard cycle or debulk cycle, heat and pressure
compact preform foam, forcing the z-pins into the composite
(b)
Remove & Discard Foam
Cured 2-Pinned Composite
Stage 3: Remove compacted foam and discard. Finish with
cured z-pinned composite.
(c)
Figure 9.2 Schematic of the Z-fiberTM insertion process using an autoclave (Adapted
from Freitas et al., 1994)