Page 82 - 3D Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
P. 82
Micromechanics Models for Mechanical Properties 71
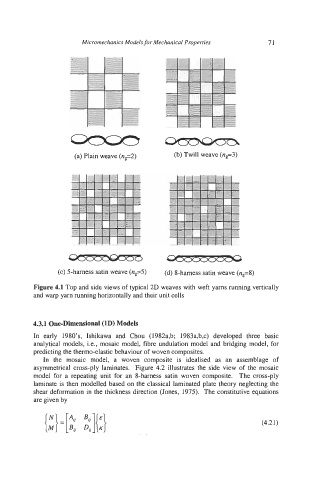
(a) Plain weave (n6=2) (b) Twill weave (n6=3)
(c) 5-harness satin weave (n+) (d) 8-harness satin weave (n,=8)
Figure 4.1 Top and side views of typical 2D weaves with weft yarns running vertically
and warp yarn running horizontally and their unit cells
4.3.1 One-Dimensional (1D) Models
In early 1980's, Ishikawa and Chou (1982a,b; 1983a,b,c) developed three basic
analytical models, Le., mosaic model, fibre undulation model and bridging model, for
predicting the thermo-elastic behaviour of woven composites.
In the mosaic model, a woven composite is idealised as an assemblage of
asymmetrical cross-ply laminates. Figure 4.2 illustrates the side view of the mosaic
model for a repeating unit for an 8-harness satin woven composite. The cross-ply
laminate is then modelled based on the classical laminated plate theory neglecting the
shear deformation in the thickness direction (Jones, 1975). The constitutive equations
{;}=Ab "I{')
are given by
B, D, K (4.21)