Page 409 - A Comprehensive Guide to Solar Energy Systems
P. 409
418 A COmpREHENSIvE GUIDE TO SOLAR ENERGy SySTEmS
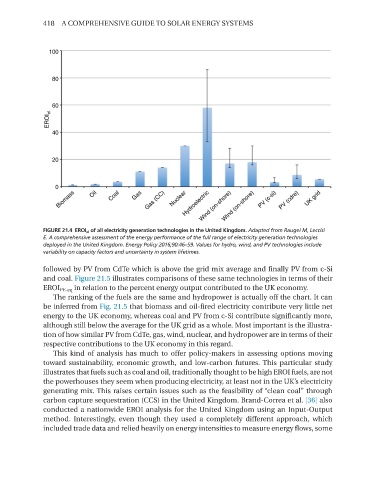
FIGURE 21.4 EROI el of all electricity generation technologies in the United Kingdom. Adapted from Raugei M, Leccisi
E. A comprehensive assessment of the energy performance of the full range of electricity generation technologies
deployed in the United Kingdom. Energy Policy 2016;90:46–59. Values for hydro, wind, and PV technologies include
variability on capacity factors and uncertainty in system lifetimes.
followed by pv from CdTe which is above the grid mix average and finally pv from cSi
and coal. Figure 21.5 illustrates comparisons of these same technologies in terms of their
EROI pEeq in relation to the percent energy output contributed to the UK economy.
The ranking of the fuels are the same and hydropower is actually off the chart. It can
be inferred from Fig. 21.5 that biomass and oilfired electricity contribute very little net
energy to the UK economy, whereas coal and pv from cSi contribute significantly more,
although still below the average for the UK grid as a whole. most important is the illustra
tion of how similar pv from CdTe, gas, wind, nuclear, and hydropower are in terms of their
respective contributions to the UK economy in this regard.
This kind of analysis has much to offer policymakers in assessing options moving
toward sustainability, economic growth, and lowcarbon futures. This particular study
illustrates that fuels such as coal and oil, traditionally thought to be high EROI fuels, are not
the powerhouses they seem when producing electricity, at least not in the UK’s electricity
generating mix. This raises certain issues such as the feasibility of “clean coal” through
carbon capture sequestration (CCS) in the United Kingdom. BrandCorrea et al. [36] also
conducted a nationwide EROI analysis for the United Kingdom using an InputOutput
method. Interestingly, even though they used a completely different approach, which
included trade data and relied heavily on energy intensities to measure energy flows, some