Page 483 - A Comprehensive Guide to Solar Energy Systems
P. 483
496 A CoMPrEhEnsiVE GUidE To solAr EnErGy sysTEMs
r(1 +r ) T
K (1 +r ) T − 1 +C
LCOEDKr(1+r)T(1+r)T−1+C(MW LCOE D = (25.9)
hD⋅365) ( MWh .365)
D
where MWh D is the daily megawatt hours of energy output given ambient conditions on a
particular day, and all other terms are as defined for Eq. (25.1).
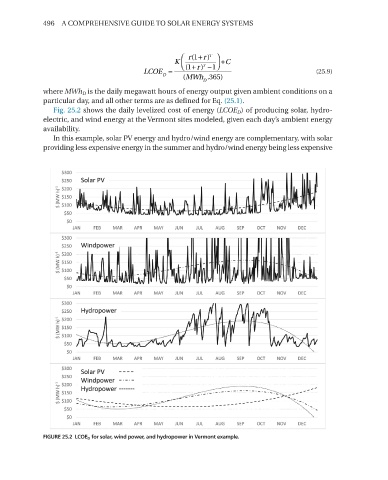
Fig. 25.2 shows the daily levelized cost of energy (LCOE D ) of producing solar, hydro-
electric, and wind energy at the Vermont sites modeled, given each day’s ambient energy
availability.
in this example, solar PV energy and hydro/wind energy are complementary, with solar
providing less expensive energy in the summer and hydro/wind energy being less expensive
FIGURE 25.2 LCOE D for solar, wind power, and hydropower in Vermont example.