Page 76 - Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery Using Smart Waterflooding
P. 76
68 Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery using Smart Waterflooding
(A) (B)
1000 10000
0.1 wt% NaCl
500ppm 0.5 wt% NaCl
1000ppm
1 wt% NaCl
2000ppm
Shear Viscosity,cP 10 Shear Viscosity,cP 100
1000
2 wt% NaCl
3000ppm
4 wt% NaCl
100
Dot : Experiment Data 10 Dot : Experiment Data
Line : Carreau Model Fit Line : Carreau Model Fit
1 1
0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000
Shear Rate, s –1 Shear Rate, s –1
(C) (D)
1000 1000
0 wt% Ca++ 25°C
0.5 wt% Ca++ 50°C
0.1 wt% Ca++ 100 70°C
Shear Viscosity,cP 10 Shear Viscosity,cP 10
90°C
0.15 wt% Ca++
100
Dot : Experiment Data Dot : Experiment Data
Line : Carreau Model Fit Line : Carreau Model Fit
1 1
0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000
Shear Rate, s –1 Shear Rate, s –1
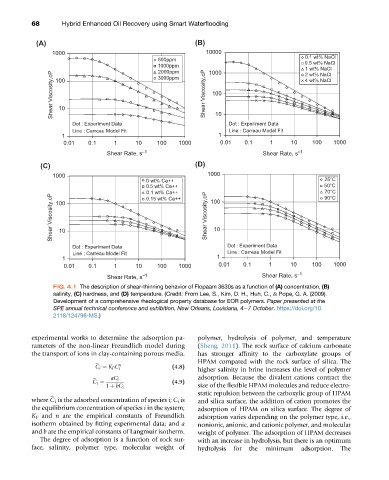
FIG. 4.1 The description of shear-thinning behavior of Flopaam 3630s as a function of (A) concentration, (B)
salinity, (C) hardness, and (D) temperature. (Credit: From Lee, S., Kim, D. H., Huh, C., & Pope, G. A. (2009).
Development of a comprehensive rheological property database for EOR polymers. Paper presented at the
SPE annual technical conference and exhibition, New Orleans, Louisiana, 4e7 October. https://doi.org/10.
2118/124798-MS.)
experimental works to determine the adsorption pa- polymer, hydrolysis of polymer, and temperature
rameters of the non-linear Freundlich model during (Sheng, 2011). The rock surface of calcium carbonate
the transport of ions in clay-containing porous media. has stronger affinity to the carboxylate groups of
HPAM compared with the rock surface of silica. The
b C i ¼ K F C n (4.8)
i higher salinity in brine increases the level of polymer
adsorption. Because the divalent cations contract the
aC i
b C i ¼ (4.9)
1 þ bC i size of the flexible HPAM molecules and reduce electro-
static repulsion between the carboxylic group of HPAM
where C i is the adsorbed concentration of species i; C i is and silica surface, the addition of cation promotes the
b
the equilibrium concentration of species i in the system; adsorption of HPAM on silica surface. The degree of
K F and n are the empirical constants of Freundlich adsorption varies depending on the polymer type, i.e.,
isotherm obtained by fitting experimental data; and a nonionic, anionic, and cationic polymer, and molecular
and b are the empirical constants of Langmuir isotherm. weight of polymer. The adsorption of HPAM decreases
The degree of adsorption is a function of rock sur- with an increase in hydrolysis, but there is an optimum
face, salinity, polymer type, molecular weight of hydrolysis for the minimum adsorption. The