Page 158 - A Practical Introduction to Optical Mineralogy
P. 158
THE NON-SILICATES
SULPHIDES
Polished
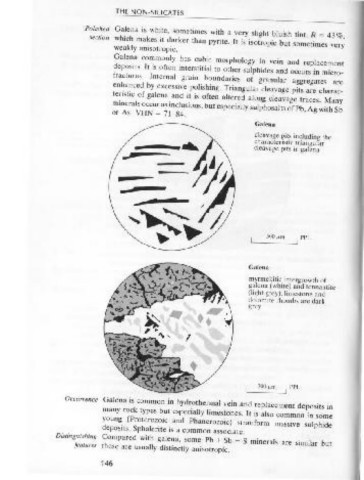
Ga!ena is whi_te, sometimes with a very slight bluish tint. R = %
section 43 Marcasite FeS2
which ma~es It d_arker than pyrite. It is isotropic but sometimes very'
weakly anisotropic. Crystals Marcasite is orthorhombic, a : b : c = 0.8194: 1:0.6245. It is commonly
tabular { 010} but may be pyramidal. Aggregates are often globular or
Galen_a co~monly has cubic morphology in vein and replacement
depositS. It IS often inte~stitial to other sulphides and occurs in micro- stalactitic. Twinning on { 101} is common, often repeated, producing
cockscomb pseudo-hexagonal shapes. Cleavage on { 101} is distinct.
fractures. Internal . gram . b~undaries of granular aggregates are
D = 4.88.
en~a~ced by excessive pohshmg. Triangular cleavage pits are charac-
Thin section Marcasite is opaque, but because of ready oxidation a brown staining of
te~Istlc of galena . and i_t is often altered along cleavage traces. Many
mmerals occur as mcluswns, but especially sulphosalts of Pb Ag with Sb limonite is often associated with it.
or As. VHN = 71-84. ' Polished section Marcasite is white, slightly yellowish. There is a weak pleochroism, lkz
pinkish white and lib and lie yellowish white. R = 49-55 %, very close to
Galena
pyrite. The strong anisotropy of marcasite in very bright bluish and
cleavage pits including the
characteristic triangular greenish greys and browns is one of the most distinctive features .
cleavage pits in galena Occurrence Marcasite often appears as lath-shaped crystals in radiating aggregates
of twins. Colloform aggregates with pyrite are common. Lamellar twin-
ning and cleavage pits may be present. VHN = 941-1288.
Distinguishing Marcasite often occurs as concretions in sedimentary rocks. It is usually
features associated with pyrite in low temperature sulphide deposits.
Compared with marcasite, pyrite is yellower, slightly softer and weakly
a m
anisotropic or isotropic; pyrrhotite is darker, brownish, softer and has a
weaker anisotropy; and arsenopyrite is whiter, brighter and has a
weaker anisotropy .
.___s_oo_,..._m _ _jl PPL
Molybdenite MoS2
Galena Molybdenite may contain Rh.
Crystals Molybdenite is hexagonal, a :c = 1:3.815. Having a layer structure, it
myrmekitic intergrowth of
galena (wh1te) and tennantite commonly has a hexagonal tabular or a short barrel shaped prismatic
(light grey): limestone and habit. It is commonly foliated massive or in scales. There is a perfect
dolomite rhombs are dark
grey basal { 0001} cleavage. D = 4. 7.
Thin section Molybdenite is opaque in the visible but it is transparent and uniaxial
- ve in the infrared.
Polished Molybdenite is bireflecting with R 0 = 3 7% (white, less bright than
section galena) and R . = 15 % (grey, similar to sphalerite). Anisotropy is very
strong with slightly pinkish white tints. Extinction is parallel to cleavage
(the brighter R 0 orientation) but is often undulatory because of defor-
mation.
It occurs as flakes or platelets with hexagonal basal sections. Well-
300 iJ.m I PPL developed basal cleavage often results in a poor polish, especially on
Occurrence grains which have their cleavage parallel to the polished surface.
Galena is common in hydrothermal vein and replacement deposits in
Deformation twinning-like structure is related to buckling of cleavage.
many rock types b_ut especially limestones. It is also common in some
VHN = 16-191 cleavage, 21-2811 cleavage.
young_ (Proteroz?Ic. and Phanerozoic) stratiform massive sulphide Occurrence Molybdenite is found in high temperature hydrothermal veins and
deposits. Sphalente IS a common associate.
Distinguishing quartz pegmatites, with Bi, Te, Au, Sn and W minerals. It also occurs in
Compared with galena, some Pb + Sb + S .
features mmerals are similar but porphyry copper style deposits. It is an accessory mineral in acid igneous
these are usually distinctly anisotropic.
rocks and occasionally is a detrital mineral.
146
147