Page 88 - A Practical Introduction to Optical Mineralogy
P. 88
SILICATE MINERALS FELDSPAR GROUP
20 o<<'U RRENCE The alkali feldspars are essential constituents of alkali and acid igneous
~
V>
rocks, particularly syenites, granites and granodiorites, felsites and
~ 18
Ol) low T orthoclase porphyries and trachytes, rhyolites and dacites. Alkali feld-
Q)
::::, 16 spars are common in pegmatites, in hydrothermal veins and in high
s 14 grade gneisses. Plutonic rocks contain orthoclase, microcline and perth-
e 12 ites whereas extrusive rocks contain sanidine and other ' high' types.
c:
0 10 Perthite types can be correlated, based on the size of the exsolved phase,
c:
.g 1------- with decreasing temperature of formation and length of time of cooling
u 8 period from cryptoperthites ( < 5 nm obtained by X-ray diffraction
c:
x data) found in hypabyssal rocks, to macroperthites (> 0.1 mm), which
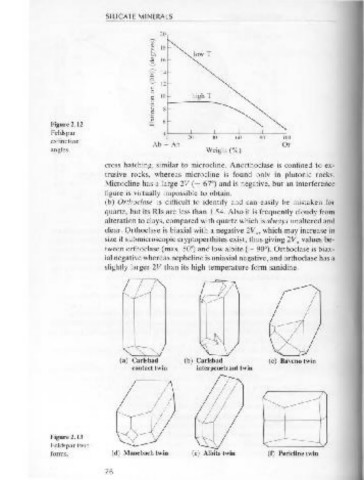
Figure 2.12 u.J 6
occur in igneous rocks formed from large plutonic intrusions.
Feldspar 40~--~~--~~--~~--~~--~
Some pegmatites contain intergrowths of alkali feldspar and quartz
extinction
Ab + An called graphic intergrowth (because the quartz crystals resemble writ-
angles. Weight(% )
ing), and may be due either to simultaneous crystallisation of alkali
cross hatching, similar to microcline. Anorthoclase is confined to ex- feldspar and quartz or to the replacement of some of the alkali feldspar
trusive rocks, whereas microcline is found only in plutonic rocks. by quartz. Associations of feldspar , usually plagioclase but occasionally
Microcline has a large 2V (- 67°) and is negative, but an interference alkali feldspar, and quartz in which the feldspar and quartz are inter-
figure is virtually impossible to obtain. calated in 'stringer' -like textures, are called myrmekite. In Rapakivi
(b) Orthoclase is difficult to identify and can easily be mistaken for granites, large crystals of alkali feldspar are mantled by plagioclase, and
quartz, but its Rls are less than 1.54. Also it is frequently cloudy from similar relationships occur in other orbicular granites. Potassium
alteration to clays, compared with quartz which is always unaltered and feldspars are common in high grade metamorphic rocks. It is a stable
clear. Orthoclase is biaxial with a negative 2V. , which may increase in mineral at the highest grades when the breakdown of muscovite leads to
size if submicroscopic cryptoperthites exist, thus giving 2V. values be- the presence of K-feldspar, with sillimanite also being formed:
tween orthoclase (max. 50°) and low albite (- 90°). Orthoclase is biax-
ial negative whereas nepheline is uniaxial negative, and orthoclase has a muscovite + Qz ~ K-feldspar + sillimanite
slightly larger 2V than its high temperature form sanidine.
These high grade metamorphic rocks containing K-feldspar include
charnockites, sillimanite gneisses, migmatites, and granulites.
Orthoclase and microcline occur as detrital grains in terrigeneous
arenaceous rocks; authigenic alkali feldspars , forming at low tempera-
tures within sediments, have been recognised which are usually
homogeneous (non-perthitic) and untwinned.
Carlsbad (b) Carlsbad (c) Baveno twin
contact twin interpenetrant twin
Figure 2.13
Feldspar twin
forms. (d) Manebach twin (e) Albite twin (f) Pericline twin
76 77