Page 53 - Quick Guide to Welding and Weld Inspection by S.E. Hughes, Clifford Matthews
P. 53
A Quick Guide to Welding and Weld Inspection
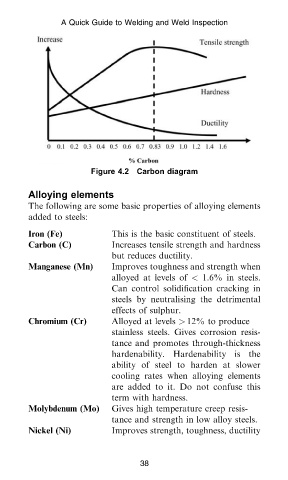
Figure 4.2 Carbon diagram
Alloying elements
The following are some basic properties of alloying elements
added to steels:
Iron (Fe) This is the basic constituent of steels.
Carbon (C) Increases tensile strength and hardness
but reduces ductility.
Manganese (Mn) Improves toughness and strength when
alloyed at levels of < 1.6% in steels.
Can control solidification cracking in
steels by neutralising the detrimental
effects of sulphur.
Chromium (Cr) Alloyed at levels > 12% to produce
stainless steels. Gives corrosion resis-
tance and promotes through-thickness
hardenability. Hardenability is the
ability of steel to harden at slower
cooling rates when alloying elements
are added to it. Do not confuse this
term with hardness.
Molybdenum (Mo) Gives high temperature creep resis-
tance and strength in low alloy steels.
Nickel (Ni) Improves strength, toughness, ductility
38
Woodhead Publishing Ltd – A Quick Guide to Welding and Weld Inspection
Data Standards Ltd, Frome, Somerset – 17/9/200904QG Welding chap4.3d Page 38 of 48