Page 181 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 181
172 3. NOISE IN MARINE SEISMICS
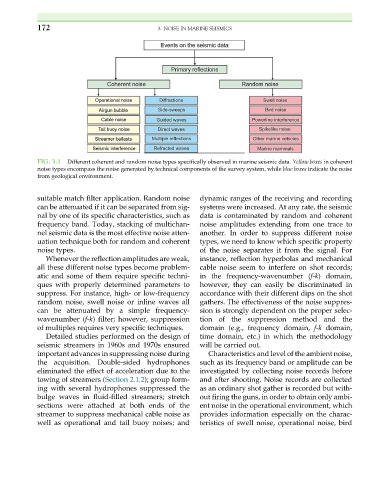
FIG. 3.1 Different coherent and random noise types specifically observed in marine seismic data. Yellow boxes in coherent
noise types encompass the noise generated by technical components of the survey system, while blue boxes indicate the noise
from geological environment.
suitable match filter application. Random noise dynamic ranges of the receiving and recording
can be attenuated if it can be separated from sig- systems were increased. At any rate, the seismic
nal by one of its specific characteristics, such as data is contaminated by random and coherent
frequency band. Today, stacking of multichan- noise amplitudes extending from one trace to
nel seismic data is the most effective noise atten- another. In order to suppress different noise
uation technique both for random and coherent types, we need to know which specific property
noise types. of the noise separates it from the signal. For
Whenever the reflection amplitudes are weak, instance, reflection hyperbolas and mechanical
all these different noise types become problem- cable noise seem to interfere on shot records;
atic and some of them require specific techni- in the frequency-wavenumber (f-k) domain,
ques with properly determined parameters to however, they can easily be discriminated in
suppress. For instance, high- or low-frequency accordance with their different dips on the shot
random noise, swell noise or inline waves all gathers. The effectiveness of the noise suppres-
can be attenuated by a simple frequency- sion is strongly dependent on the proper selec-
wavenumber (f-k) filter; however, suppression tion of the suppression method and the
of multiples requires very specific techniques. domain (e.g., frequency domain, f-k domain,
Detailed studies performed on the design of time domain, etc.) in which the methodology
seismic streamers in 1960s and 1970s ensured will be carried out.
important advances in suppressing noise during Characteristics and level of the ambient noise,
the acquisition. Double-sided hydrophones such as its frequency band or amplitude can be
eliminated the effect of acceleration due to the investigated by collecting noise records before
towing of streamers (Section 2.1.2); group form- and after shooting. Noise records are collected
ing with several hydrophones suppressed the as an ordinary shot gather is recorded but with-
bulge waves in fluid-filled streamers; stretch out firing the guns, in order to obtain only ambi-
sections were attached at both ends of the ent noise in the operational environment, which
streamer to suppress mechanical cable noise as provides information especially on the charac-
well as operational and tail buoy noises; and teristics of swell noise, operational noise, bird