Page 78 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 78
2.2 AIR GUN ARRAYS 69
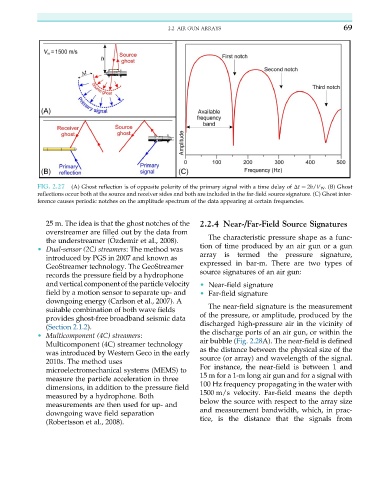
FIG. 2.27 (A) Ghost reflection is of opposite polarity of the primary signal with a time delay of Δt ¼ 2h/V W . (B) Ghost
reflections occur both at the source and receiver sides and both are included in the far-field source signature. (C) Ghost inter-
ference causes periodic notches on the amplitude spectrum of the data appearing at certain frequencies.
25 m. The idea is that the ghost notches of the 2.2.4 Near-/Far-Field Source Signatures
overstreamer are filled out by the data from
€
the understreamer (Ozdemir et al., 2008). The characteristic pressure shape as a func-
• Dual-sensor (2C) streamers: The method was tion of time produced by an air gun or a gun
introduced by PGS in 2007 and known as array is termed the pressure signature,
expressed in bar-m. There are two types of
GeoStreamer technology. The GeoStreamer
source signatures of an air gun:
records the pressure field by a hydrophone
and vertical componentof the particle velocity • Near-field signature
field by a motion sensor to separate up- and • Far-field signature
downgoing energy (Carlson et al., 2007). A
suitable combination of both wave fields The near-field signature is the measurement
provides ghost-free broadband seismic data of the pressure, or amplitude, produced by the
(Section 2.1.2). discharged high-pressure air in the vicinity of
the discharge ports of an air gun, or within the
• Multicomponent (4C) streamers:
air bubble (Fig. 2.28A). The near-field is defined
Multicomponent (4C) streamer technology
as the distance between the physical size of the
was introduced by Western Geco in the early
source (or array) and wavelength of the signal.
2010s. The method uses
For instance, the near-field is between 1 and
microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) to
15 m for a 1-m long air gun and for a signal with
measure the particle acceleration in three
100 Hz frequency propagating in the water with
dimensions, in addition to the pressure field
1500 m/s velocity. Far-field means the depth
measured by a hydrophone. Both
below the source with respect to the array size
measurements are then used for up- and
downgoing wave field separation and measurement bandwidth, which, in prac-
(Robertsson et al., 2008). tice, is the distance that the signals from