Page 219 - Adaptive Identification and Control of Uncertain Systems with Nonsmooth Dynamics
P. 219
218 Adaptive Identification and Control of Uncertain Systems with Non-smooth Dynamics
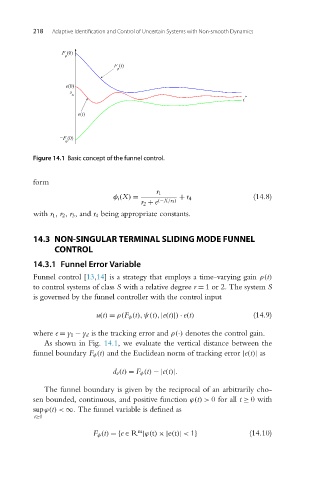
Figure 14.1 Basic concept of the funnel control.
form
r 1
φ i (X) = + r 4 (14.8)
r 2 + e (−X/r 3 )
with r 1, r 2, r 3,and r 4 being appropriate constants.
14.3 NON-SINGULAR TERMINAL SLIDING MODE FUNNEL
CONTROL
14.3.1 Funnel Error Variable
Funnel control [13,14] is a strategy that employs a time-varying gain ρ(t)
to control systems of class S with a relative degree r = 1 or 2. The system S
is governed by the funnel controller with the control input
u(t) = ρ(F φ (t),ψ(t),|e(t)|) · e(t) (14.9)
where e = y 1 − y d is the tracking error and ρ(·) denotes the control gain.
As shown in Fig. 14.1, we evaluate the vertical distance between the
funnel boundary F φ (t) and the Euclidean norm of tracking error |e(t)| as
d v (t) = F φ (t) −|e(t)|.
The funnel boundary is given by the reciprocal of an arbitrarily cho-
sen bounded, continuous, and positive function ϕ(t)> 0 for all t ≥ 0with
supϕ(t)< ∞. The funnel variable is defined as
t≥0
m
F φ (t) ={e ∈ R |ϕ(t) ×|e(t)| < 1} (14.10)