Page 320 - Adsorption by Powders and Porous Solids
P. 320
CHAPTER 10. ADSORPTlON BY METAL OXIDES 309
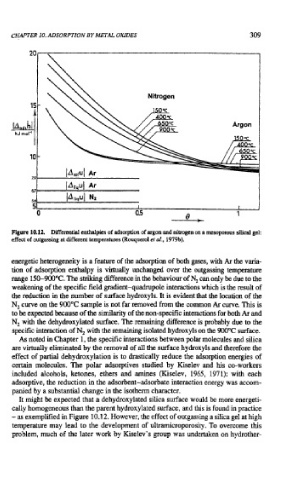
Figure 10.12. Differential enthalpies of adsorption of argon and nitrogen on a mesoporous silical gel:
effect of outgassing at different temperatures (Rouqueml er al., 1979b).
energetic heterogeneity is a feature of the adsorption of both gases, with Ar the varia-
tion of adsorption enthalpy is virtually unchanged over the outgassing temperature
range 150-900°C. The striking difference in the behaviour of N, can only be due to the
weakening of the specific field gradient-quadruple interactions which is the result of
the reduction in the number of surface hydroxyls. It is evident that the location of the
N, curve on the 900°C sample is not far removed from the common Ar curve. This is
to be expected because of the similarity of the non-specific interactions for both Ar and
N, with the dehydroxylated surface. The remaining difference is probably due to the
specific interaction of N, with the remaining isolated hydroxyls on the 900°C surface.
As noted in Chapter 1, the specific interactions between polar molecules and silica
are virtually eliminated by the removal of all the surface hydroxyls and therefore the
effect of partial dehydroxylation is to drastically reduce the adsorption energies of
certain molecules. The polar adsorptives studied by Kiselev and his co-workers
included alcohols, ketones, ethers and amines (Kiselev, 1965, 1971): with each
adsorptive, the reduction in the adsorbent-adsorbate interaction energy was accom-
panied by a substantial change in the isotherm character.
It might be expected that a dehydroxylated silica surface would be more energeti-
cally homogeneous than the parent hydroxylated surface, and this is found in practice
- as exemplified in Figure 10.12. However, the effect of outgassing a silica gel at high
temperature may lead to the development of ultramicroporosity. To overcome this
problem, much of the later work by Kiselev's group was undertaken on hydrother-