Page 89 - Adsorption by Powders and Porous Solids
P. 89
ADSORPTION BY POWDERS AND POROUS SOLIDS
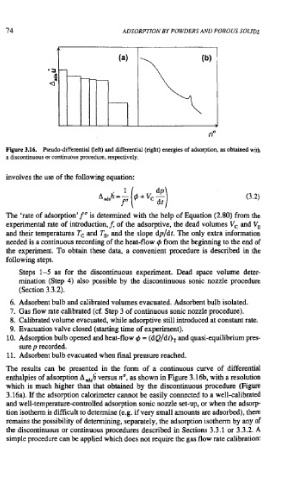
Figure 3.16. Pseudo-differential (left) and differential (right) energies of adsorption, as obtained with
a discontinuous or continuous procedure, respectively.
involves the use of the following equation:
The 'rate of adsorption'f" is determined with the help of Equation (2.80) from the
experimental rate of introduction, f, of the adsorptive, the dead volumes Vc and V,
and their temperatures Tc and T,, and the slope dp/dt. The only extra information
needed is a continuous recording of the heat-flow q5 from the beginning to the end of
the experiment. To obtain these data, a convenient procedure is described in the
following steps.
Steps 1-5 as for the discontinuous experiment. Dead space volume deter-
mination (Step 4) also possible by the discontinuous sonic nozzle procedure
(Section 3.3.2).
6. Adsorbent bulb and calibrated volumes evacuated. Adsorbent bulb isolated.
7. Gas flow rate calibrated (cf. Step 3 of continuous sonic nozzle procedure).
8. Calibrated volume evacuated, while adsorptive still introduced at constant rate.
9. Evacuation valve closed (starting time of experiment).
10. Adsorption bulb opened and heat-flow q5 = (dQ/dt), and quasi-equilibrium pres-
sure p recorded.
11. Adsorbent bulb evacuated when final pressure reached.
The results can be presented in the form of a continuous curve of differential
enthalpies of adsorption A &h versus nu, as shown in Figure 3.16b, with a resolution
which is much higher than that obtained by the discontinuous procedure (Figure
3.16a). If the adsorption calorimeter cannot be easily connected to a well-calibrated
and well-temperature-controlled adsorption sonic nozzle set-up, or when the adsorp
tion isotherm is difficult to determine (e.g. if very small amounts are adsorbed), there
remains the possibility of determining, separately, the adsorption isotherm by any of
the discontinuous or continuous procedures described in Sections 3.3.1 or 3.3.2. A
simple procedure can be applied which does not require the gas flow rate calibration: